Figure 1.
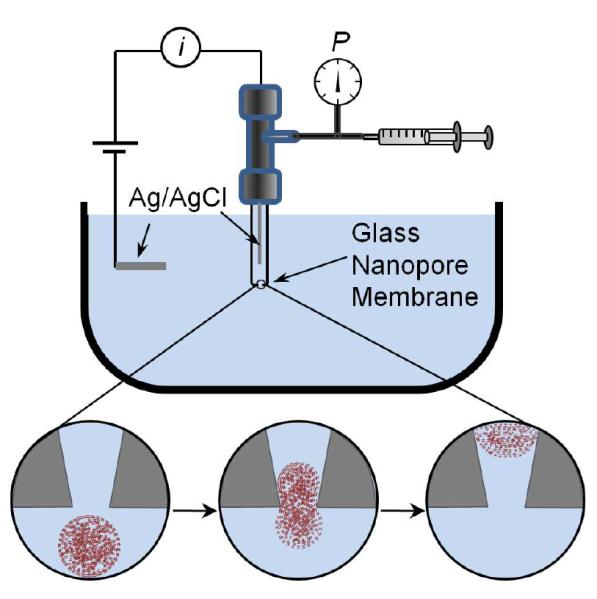
Schematic drawing of the experimental setup and microgel deformation during translocation. The glass nanopore membrane (GNM) contains a single nanopore separating two electrolyte solutions. A pressure applied across the GNM drives the external electrolyte solution containing the microgels through the nanopore. A constant voltage is applied between the Ag/AgCl electrodes to record the i-t trace.
