Figure 5.
Mad2 Overexpression Boosts Aneuploidy and Facilitates Tumor Persistence after Oncogene Withdrawal
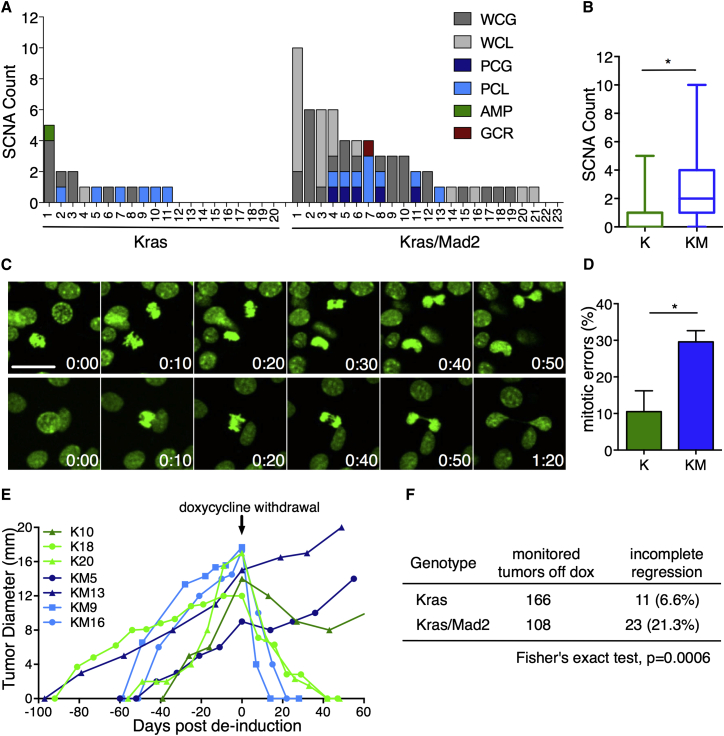
(A) SCNAs in 20 Kras and 23 Kras/Mad2 primary tumors. Shown are whole chromosome gain (WCG) and loss (WCL), partial chromosome gain (PCG) and loss (PCL), focal amplification (AMP), and gross chromosomal rearrangement (GCR, red). x Axis, individual tumors; y axis, SCNAs per tumor.
(B) Average SCNAs in K and KM tumors; Fisher’s exact test, p = 0.01039.
(C) Representative micrographs of KM tumor cells in vitro (H2B-GFP, green). Scale bar, 25 μm. Top: furrow regression and polyploidization. Bottom: lagging chromosome during anaphase and cytokinesis failure.
(D) Percentage of mitotic errors per tumor (K, n = 4, 74 cells; KM, n = 5, 84 cells); Mann-Whitney test, p = 0.0317.
(E) Representative examples of tumor development in K and KM tumors. The arrow indicates doxycycline withdrawal (day 0).
(F) Status of tumor regression in K and KM cohorts 2 months after doxycycline withdrawal.
∗p < 0.05. See also Figures S5 and S6.