Abstract
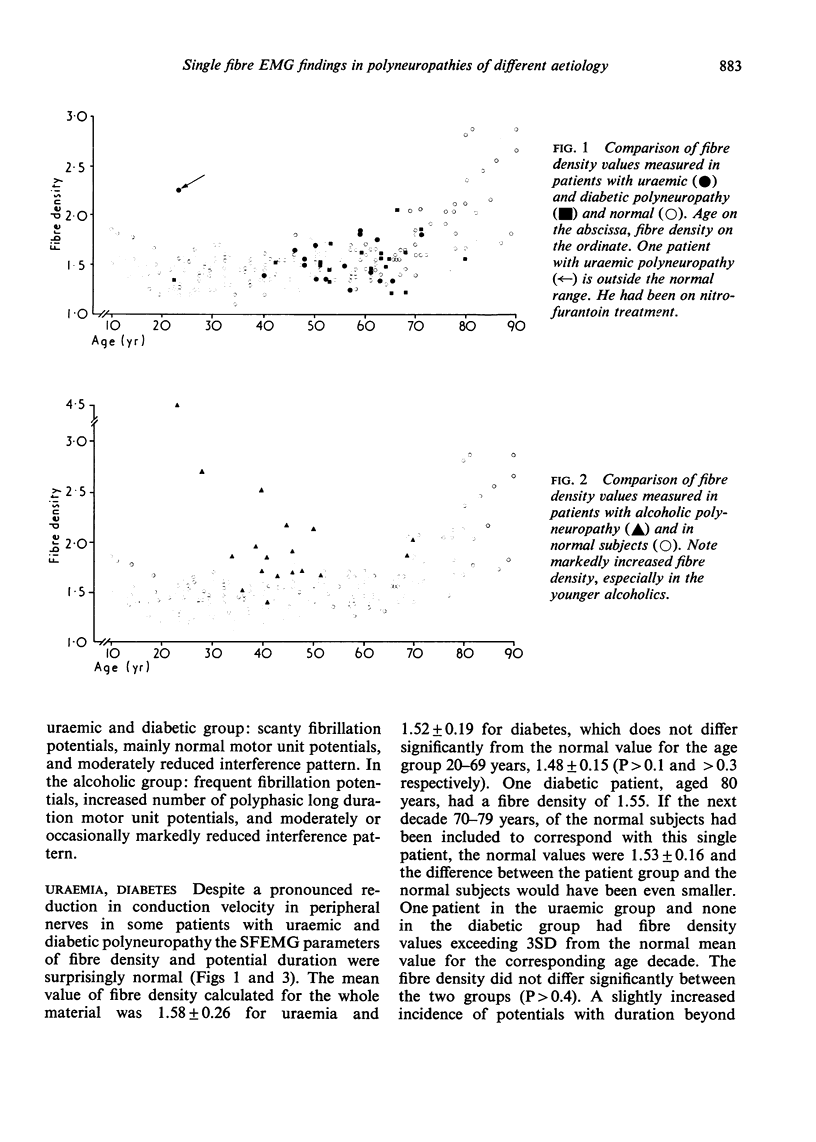
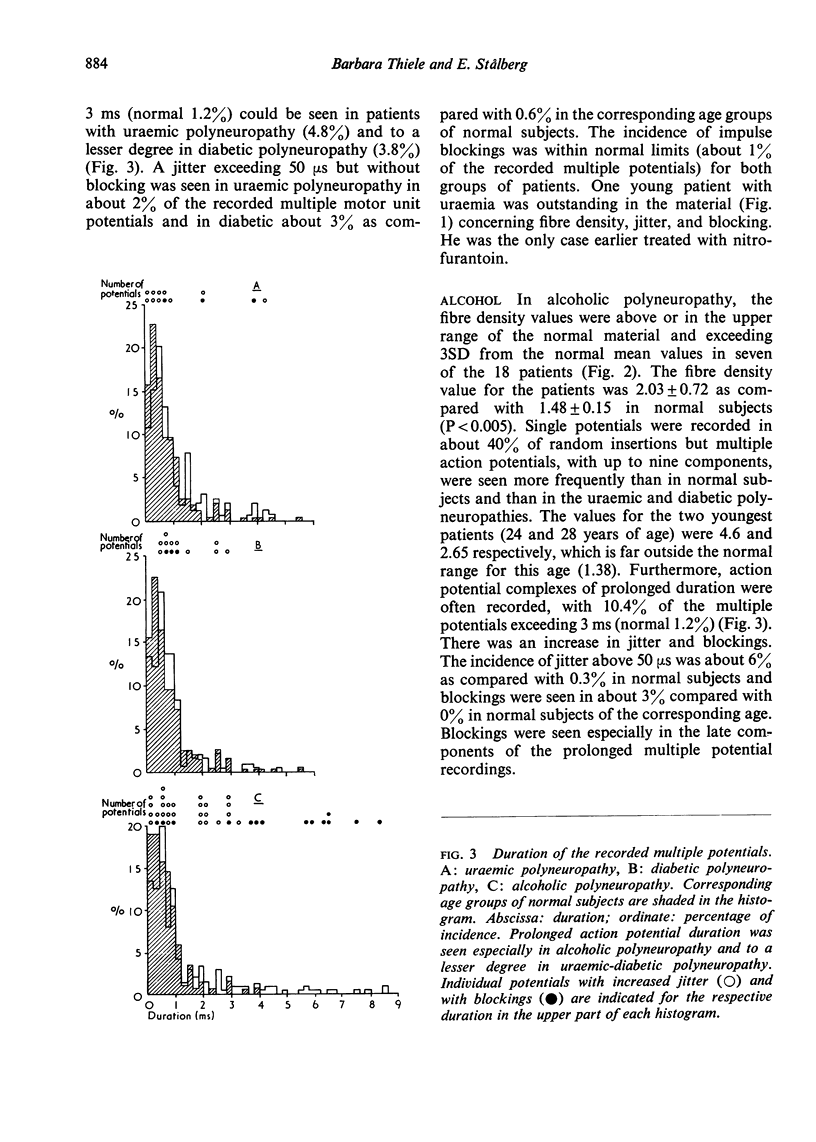
Single fibre electromyography was carried out in patients with polyneuropathy due to uraemia, diabetes, and alcohol. In the two former groups the fibre density within the motor unit and the impulse transmission were mainly normal. In the latter group the fibre density was significantly increased as signs of reinnervation. Impulse transmission was impaired in a number of the action potential complexes, which is typical of active reinnervation. The results may indicate that the diabetic and uraemic polyneuropathies are characterized in the main by demyelination, whereas the alcoholic type is dominated by axonal lesion even at an early stage.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASBURY A. K., VICTOR M., ADAMS R. D. Uremic polyneuropathy. Arch Neurol. 1963 Apr;8:413–428. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1963.00460040083008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff A. Die alkoholische Polyneuropathie. Klinische, ultrastrukturelle und pathogenetische Aspekte. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1971 Feb 19;96(8):317–passim. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1108248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAGG B. G., THOMAS P. K. CHANGES IN NERVE CONDUCTION IN EXPERIMENTAL ALLERGIC NEURITIS. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1964 Apr;27:106–115. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.27.2.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra J. S., Hurwitz L. J., Montgomery D. A. The pathogenesis of sural nerve changes in diabetes mellitus. Brain. 1969;92(2):391–418. doi: 10.1093/brain/92.2.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLMAN C. L. The morbid anatomy of diabetic neuropathy. Neurology. 1963 Feb;13:135–142. doi: 10.1212/wnl.13.2.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayan A. D., Gardner-Thorpe C., Down P. F., Gleadle R. I. Peripheral neuropathy in uremia. Pathological studies on peripheral nerves from 6 patients. Neurology. 1970 Jul;20(7):649–658. doi: 10.1212/wnl.20.7.649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinn J. J., Crane D. L. Schwann cell dysfunction in uraemia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Oct;33(5):605–608. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.5.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyck P. J., Gutrecht J. A., Bastron J. A., Karnes W. E., Dale A. J. Histologic and teased-fiber measurements of sural nerve in disorders of lower motor and primary sensory neurons. Mayo Clin Proc. 1968 Feb;43(2):81–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyck P. J., Johnson W. J., Lambert E. H., O'Brien P. C. Segmental demyelination secondary to axonal degeneration in uremic neuropathy. Mayo Clin Proc. 1971 Jun;46(6):400–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbels E., Schliep G. Diabetische Polyneuropathie: Probleme der Diagnostik und Nosologie. Dargestellt auf Grund des neueren Schrifttums und einer Analyse von 100 eigenen fällen. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr Grenzgeb. 1970 Aug;38(8):369–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliatt R. W. Applied electrophysiology in nerve and muscle disease [abridged]. Proc R Soc Med. 1966 Oct;59(10):989–993. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakelius L., Stålberg E. Electromyographical studies of free autogenous muscle transplants in man. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg. 1974;8(3):211–219. doi: 10.3109/02844317409084397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. I. Studies on demyelinated peripheral nerves in guinea-pigs with experimental allergic neuritis. A histological and electrophysiological study. II. Electrophysiological observations. Brain. 1967 Jun;90(2):313–332. doi: 10.1093/brain/90.2.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpati G., Engel W. K. "Type grouping" in skeletal muscles after experimental reinnervation. Neurology. 1968 May;18(5):447–455. doi: 10.1212/wnl.18.5.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinghardt G. W. Schädigungen des Nervensystems durch Nitrofurane bei der Ratte. Acta Neuropathol. 1967 Aug 2;9(1):18–33. doi: 10.1007/BF00688155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knill-Jones R. P., Goodwill C. J., Dayan A. D., Williams R. Peripheral neuropathy in chronic liver disease: clinical, electrodiagnostic, and nerve biopsy findings. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1972 Feb;35(1):22–30. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.35.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann H. J., Tackmann W. Die Ubermittlung frequenter Impulsserien in demyelinisierten und in degenerierenden Nervenfasern. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr (1970) 1970;213(3):215–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00342658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reske-Nielsen E., Lundbaek K., Gregersen G., Harmsen A. Pathological changes in the central and peripheral nervous system of young long-term diabetics. The terminal neuro-muscular apparatus. Diabetologia. 1970 Apr;6(2):98–103. doi: 10.1007/BF00421436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHALAEPFER W. W., HAGER H. ULTRASTRUCTURAL STUDIES OF INH-INDUCED NEUROPATHY IN RATS. I. EARLY AXONAL CHANGES. Am J Pathol. 1964 Aug;45:209–219. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stålberg E., Ekstedt J., Broman A. The electromyographic jitter in normal human muscles. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1971 Nov;31(5):429–438. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(71)90164-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stålberg E., Thiele B. Motor unit fibre density in the extensor digitorum communis muscle. Single fibre electromyographic study in normal subjects at different ages. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Sep;38(9):874–880. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.9.874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stålberg E., Thiele B. Transmission block in terminal nerve twigs: a single fibre electromyographic finding in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1972 Feb;35(1):52–59. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.35.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS P. K., LASCELLES R. G. SCHWANN-CELL ABNORMALITIES IN DIABETIC NEUROPATHY. Lancet. 1965 Jun 26;1(7400):1355–1357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)92154-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS P. K., SEARS T. A., GILLIATT R. W. The range of conduction velocity in normal motor nerve fibers to the small muscles of the hand and foot. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1959 Aug;22:175–181. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.22.3.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. C., McLeod J. G. Alcoholic neuropathy. An electrophysiological and histological study. J Neurol Sci. 1970 May;10(5):457–469. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(70)90025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller R. O., Nester B. Early changes at the node of Ranvier in segmental demyelination. Histochemical and electron microscopic observations. Brain. 1972;95(4):665–674. doi: 10.1093/brain/95.4.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


