Figure 3. Dlx1−/−;Dlx2+/− compound mutants have defects in the laminar position of immature cortical interneurons.
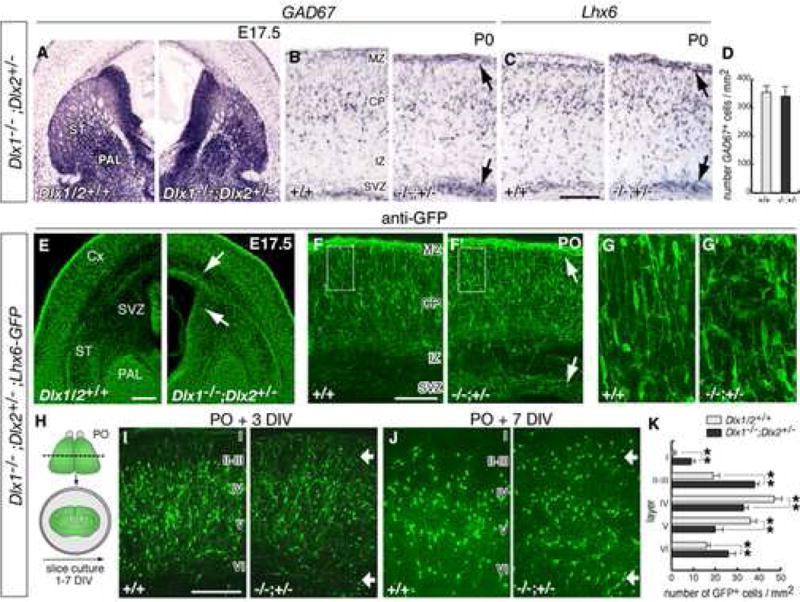
(A) mRNA in situ hybridization for GAD67 in coronal sections though the basal ganglia of a Dlx1−/−;Dlx2+/− mutant and a control embryo at E17.5 (abbreviations: Cx, cortex; PAL: globus pallidus; ST, striatum).
(B, C) GAD67 and Lhx6 expression in coronal sections through neocortex at P0, showing accumulation of GAD67+ cells and Lhx6+ cells in the SVZ and MZ (black arrows; abbreviations: SVZ, subventricular zone; IZ, intermediate zone; CP, cortical plate; MZ, marginal zone).
(D) Quantification of total numbers of GAD67+ neurons in control and mutant P0 neocortex.
(E–G) Histological analysis of Dlx1−/−;Dlx2+/−;Lhx6-GFP+ embryos. (E) shows GFP expression in the globus pallidus (PAL) and in interneurons migrating to neocortex. (F, F′) are coronal sections through neocortex at P0. Arrows in (E, F) indicate increased numbers of GFP+ cells in the subpallial SVZ, and in the cortical SVZ and MZ. (G, G′) are higher magnifications of the areas boxed in (F, F′), showing the morphology of GFP+ cells in the cortical plate.
(H) Experimental assay used to examine the laminar positions of interneurons in neocortex.
(I–J) Coronal sections through the neocortex from organotypic cultures prepared from P0 brains and maintained 3 and 7 DIV. Roman numbers approximate the position of cortical layers. Arrows indicate accumulation of GFP+ neurons in superficial (I–III) and deep (VI) layers of mutant brains.
(K) Quantification of the distribution of GFP+ cells in neocortical layers of control and Dlx1−/−;Dlx2+/− organotypic cultures after 7 DIV (controls: I: 0.15 ± 0.13; II–III: 19.1 ± 2.3; IV: 47.3 ± 4.9; V: 36.6 ± 3.7; VI: 16.1 ± 2.1; mutants: I: 9.3 ± 1.9, p < 0.01; II–III: 38.5 ± 2.5, p < 0.01; IV: 33.4 ± 2.8, p < 0.01; V: 19.9 ± 4.0, p < 0.01; VI: 26.2 ± 4.8, p < 0.01; n = 7, each genotype). ** p < 0.01 (Student’s t test). Scale bars = 500 μm (A,E) and 250 μm (B,C,F,G and I,J).
