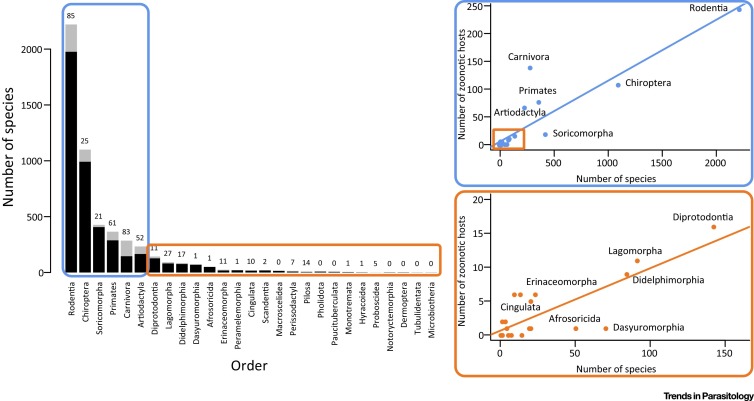
Figure 2.
The Number of Zoonotic Hosts Increases with Total Species Richness of the Order. Zoonotic diseases are found in the majority of terrestrial mammal orders (21/27), with the most species-rich orders containing the greatest diversity of zoonoses. This split bar plot shows the total number of host species (black and grey) and the fraction of species that are confirmed zoonotic hosts for one or more zoonotic diseases (grey). The number above each bar represents a tally of the total unique zoonoses per order. Mammal orders are arranged in descending order of species richness. The number of zoonotic host species in each order is represented by scatterplots, with the most-speciose orders being contained in the blue boxes (top right; regression R2 = 0.81) and all other orders in the orange boxes (bottom right; regression R2 = 0.63).