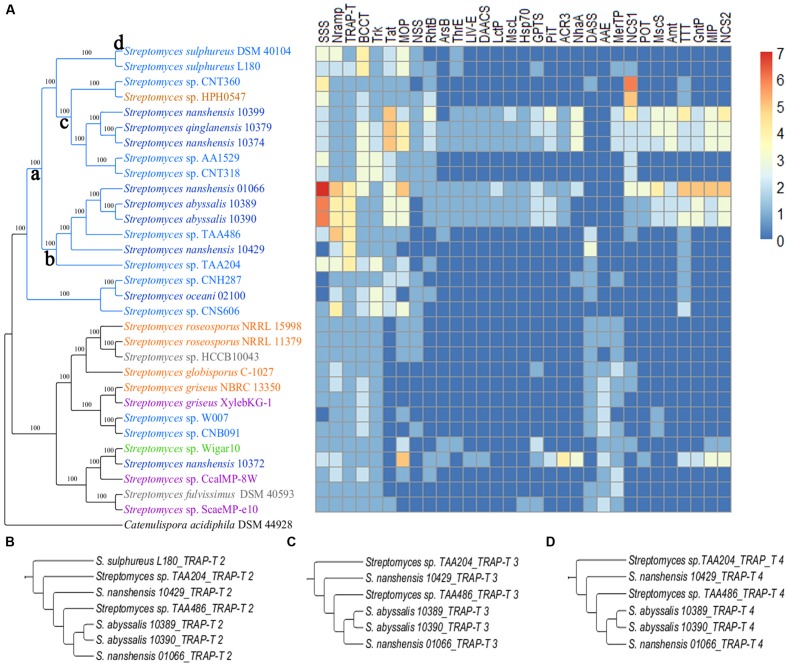
FIGURE 7.
(A) A streptomycete species tree and a heatmap showing the distribution of transport protein families. The transport protein families are described as follows: SSS, solute: sodium symporter; Nramp, metal ion (Mn2+-iron) transporter; TRAP-T, tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic transporter; BCCT, betaine/carnitine/choline transporter; Trk, K+ transporter; Tat, twin arginine targeting; MOP, multidrug/oligosaccharidyl-lipid/polysaccharide; NSS, neurotransmitter: sodium symporter; RhtB, resistance to homoserine/threonine; ArsB, arsenite-antimonite; ThrE, threonine/serine exporter; LIV-E, branched chain amino acid exporter; DAACS, dicarboxylate/amino acid: cation (Na+ or H+) symporter; LctP, lactate permease; MscL, large conductance mechanosensitive ion channel; Hsp70, cation channel-forming heat shock protein-70; GPTS, general phosphotransferase system; PiT, the inorganic phosphate transporter; ACR3, arsenical resistance-3; NhaA, Na+: H+ antiporter; DASS, divalent anion: Na+ symporter; AAE, aspartate: alanine exchanger; MerTP, mercuric ion (Hg2+) permease; NCS1, nucleobase: cation symporter-1; POT, proton-dependent oligopeptide transporter; MscS, small conductance mechanosensitive ion channel; Amt, ammonia transporter channel; TTT, tricarboxylate transporter; GntP, gluconate: H+ symporter; MIP, the major intrinsic protein; and NCS2, the nucleobase:cation symporter-2. (B) The gene tree of TRAP-T 2. (C) The gene tree of TRAP-T 3. (D) The gene tree of TRAP-T 4.