Figure 2.
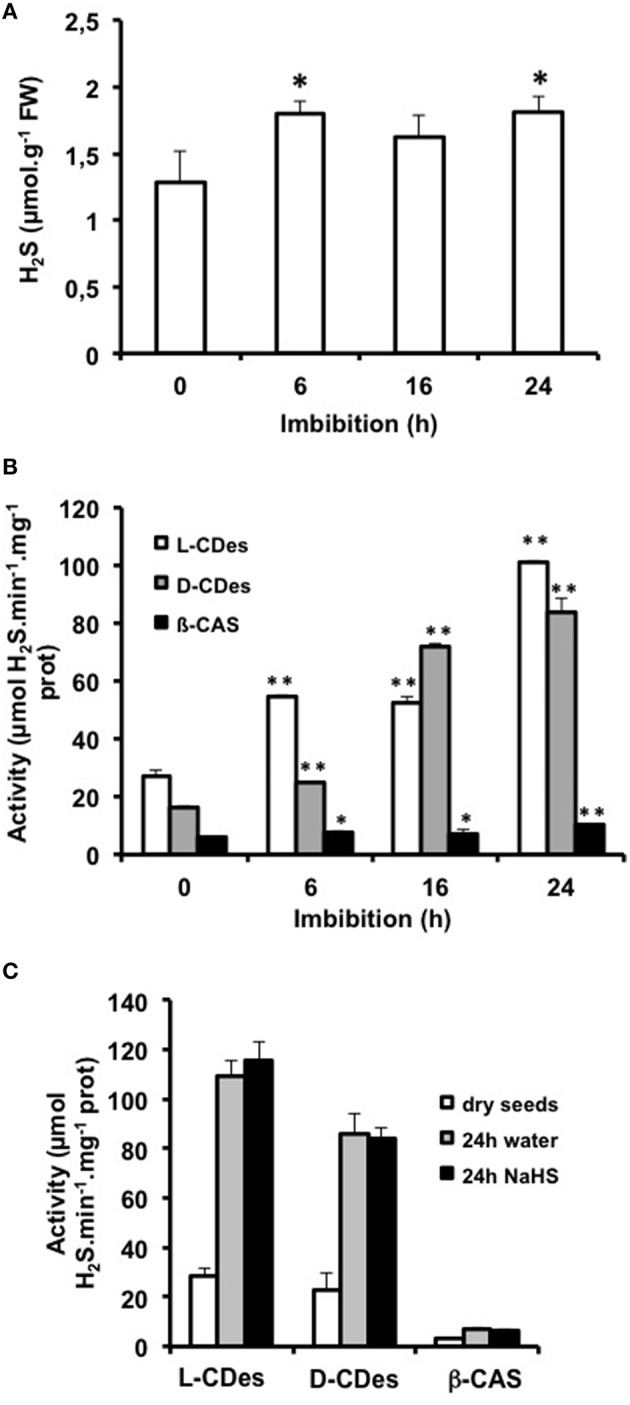
H2S synthesis during Arabidopsis seed imbibition. (A) Evolution of Arabidopsis seed H2S content during imbibition. Seeds were imbibed on distilled water in the dark at 15°C. Values are mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments. Asterisks represent statistical differences relative to H2S content in dry seeds (Student's test; *P < 0.05); (B) Evolution of the activities of H2S-generating enzymes in imbibed Arabidopsis seeds. Seeds were imbibed on distilled water in the dark at 15°C for the indicated durations. Total proteins were subsequently extracted and used for the measurement of L-cysteine desulfhydrase (L-CDes, white bars), D-cysteine desulfhydrase (D-CDes, gray bars), and β-cyanoalanine synthase (β-CAS, dark bars) activities. Values are mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments. Asterisks represent statistical differences relative to the activity in dry seed protein extracts (Student's test; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01); (C) Evolution of the activities of H2S-generating enzymes in Arabidopsis seeds imbibed on water or 1 mM NaHS. Seeds were imbibed on distilled water or 1 mM NaHS in the dark at 15°C for 24 h. Total proteins were subsequently extracted and used for the measurement of L-cysteine desulfhydrase (L-CDes), D-cysteine desulfhydrase (D-CDes), and β-cyanoalanine synthase (β-CAS) activities. Activities were compared with those of dry seeds. Values are mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments.
