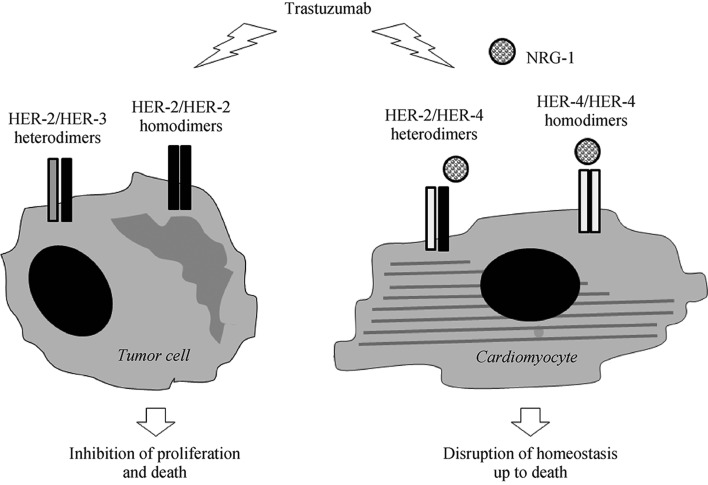
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the NRG-1/HER-2 paradigm for trastuzumab cardiotoxicity.
In oncology, trastuzumab is used to treat breast cancer in which HER-2 is overexpressed and spontaneously homodimerizes or forms heterodimers with other HER receptors, especially HER-3. As this ligand-independent activation of HER-2 sustains tumor growth and survival, trastuzumab halts the proliferation and causes the death of tumor cells (left side). In the heart, HER-2 functions as a dimerization partner of HER-4 after this latter is recruited by NRG-1 and regulates homeostatic cell responses. Off-target inhibition of cardiac HER-2 results in the disruption of part of NRG-1 dependent signaling and, eventually, in alterations of structure and function that may be lethal to cardiomyocytes (right side). HER: human epidermal growth factor receptor; NRG-1: neuregulin.