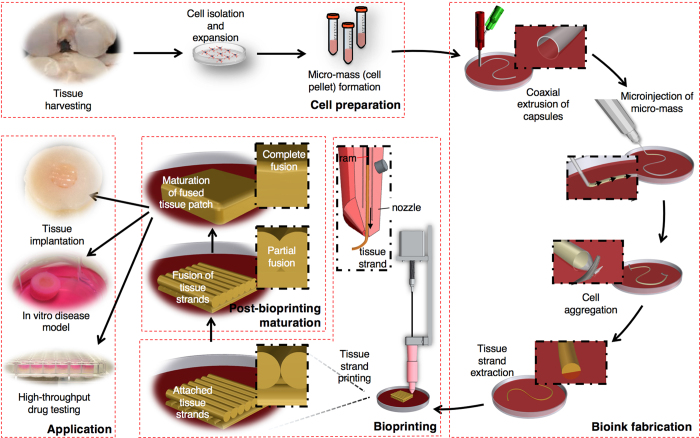
Figure 1. Schematic elucidating the concept of tissue printing using tissue strands as a new bioink.
Cells extracted from harvested tissues in large numbers are microinjected into tubular capsules, where tissue strands are obtained through aggregation of cells. Upon fabrication, scaffold-free tissue strands are printed without need for a delivering medium or a support structure for cell aggregation and tissue fusion. Printed tissue constructs are cultivated for fusion and further maturation, which can be used for various applications such as tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, in-vitro disease models, or drug screening.