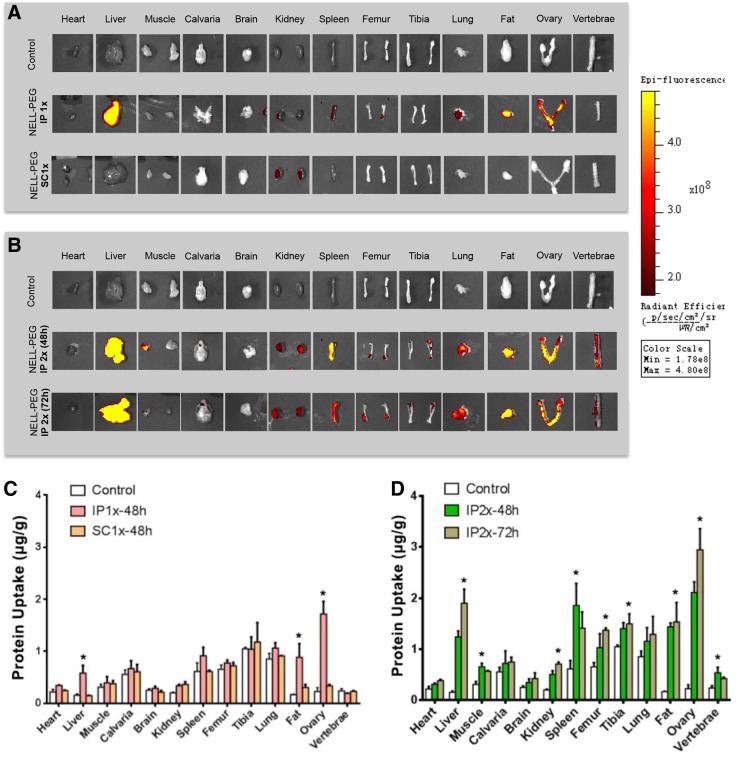
FIG. 1.
Biodistribution study was performed to compare the protein distribution of NELL-PEG labeled with VivoTag 680XL via the IP and SC administration. (A) The IP and SC routes were compared after CD-1 mice were subjected to a single dose 1 × (1.25 mg/kg) of NELL-PEG. Ex vivo images of the organs were collected at 48 h postinjection. The IP injection group showed detectable protein retention in the organs of liver, spleen, kidney, lung, fat, ovary, and femur; however, a similar finding was not observed in the SC injection group. (B) A double dose 2 × (2.5 mg/kg) of NELL-PEG was administered via the IP route, and the organs were dissected and imaged at two different time points (48 and 72 h) postinjection. (C) Quantification of the amount of protein distributed to different organs (μg/g). The biodistribution study confirmed that a single-dose injection of NELL-PEG via IP administration has significantly higher protein uptake in the liver, fat, and ovary compared with the PBS control group. (D) A double-dose injection of NELL-PEG via the IP administration showed that the quantification of the images at 48 h postinjection has significantly higher protein uptake in the targeted bone tissues, namely the femur, tibia, and vertebrae, compared with the control group. Quantification of the protein uptake at 72 h postinjection revealed a higher amount of protein in the liver and kidney compared with that at 48 h postinjection. *Significant difference (p < 0.05) between treatment and control group means. Error bars represent standard deviation. IP, intraperitoneal; NELL-PEG, PEGylation of NELL-1; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; SC, subcutaneous.