Figure 2.
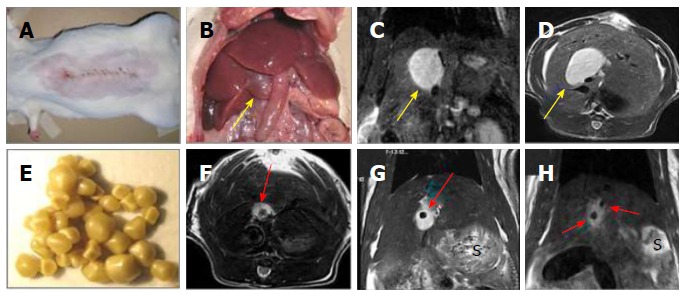
Creation of a rat model of cholelithiasis. A: Midline abdominal incision for CBD ligation; B: Laparotomy to expose the cholestasis-induced VGB (arrow); C: Coronal plane of T2-w MRI displaying an oval-shaped hyperintense dilated CBD or a VGB (arrow); D: Axial plane of T2-w MRI displaying the same oval-shaped hyperintense VGB (arrow); E: Gallstones from patients of cholelithiasis derived by cholecystectomy; F: Axial plane of T2-w MRI showing the same case in D but now implanted with a human gallstone (arrow); G: Coronal plane of T2-w MRI displaying the same case in F with a gallstone (arrow); H: Coronal plane of T2-w MRI two hypointense gallstones (arrows) located in a hyperintense VGB in another case. S denotes stomach on MR images. CBD: Common bile duct; VGB: Virtual gallbladder; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging.
