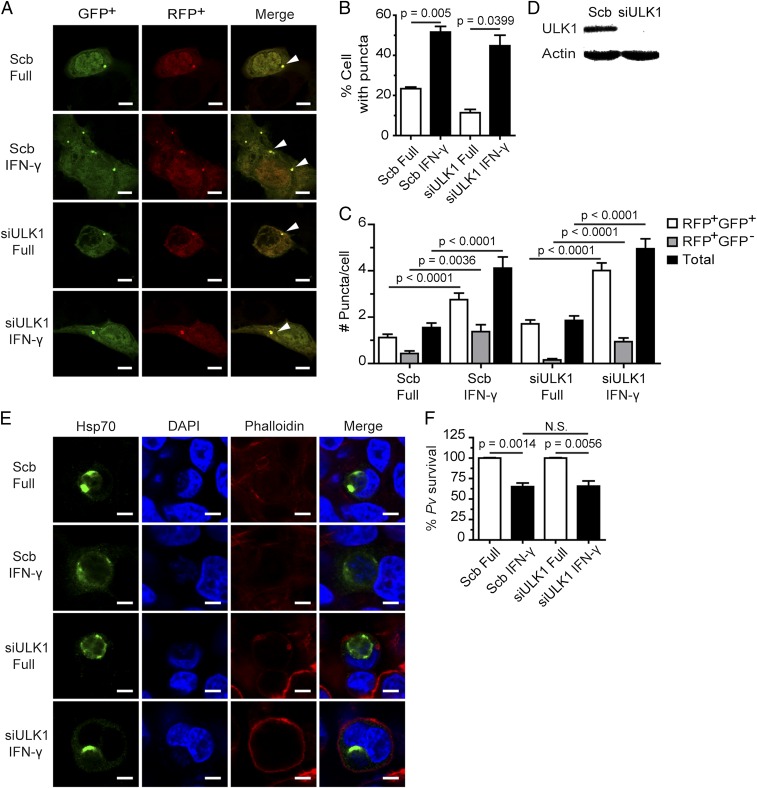
Fig. 4.
ULK1 is dispensable for the killing of liver-stage P. vivax mediated by IFN-γ. (A–C) ULK1 is not required for IFN-γ–induced LC3 puncta formation in HC04 cells. The cells were cotransfected with cDNAs encoding RFP-GFP-LC3 and either siRNAs against ULK1 or scramble control siRNAs. At 48 h posttransfection, they were treated with IFN-γ for 4 h and then processed for fluorescence microscopy analysis. RFP+GFP+-LC3 (autophagosomes) and RFP+GFP−-LC3 (autolysosomes) were quantified by determining the percentage of puncta-containing cells among at least 100 cells per condition from three independent experiments. Only puncta ≥0.25 µm in size were counted. The number of puncta per cell was also examined in Z-stack images of at least 30 cells per condition per independent experiment. Data are mean ± SEM; the results are expressed relative to the full control. (Scale bar: 5 µm.) (D) ULK1 immunoblot analysis after depletion of the protein. HC04 cells were transfected with either scramble control siRNAs or siRNAs against ULK1. At 48 h posttransfection, they were harvested for Western blot analysis. (E and F) ULK1-deficient or control HC04 cells were infected with P. vivax sporozoites at an MOI of 1, treated with IFN-γ for 4 h, washed, and then maintained in complete medium until being harvested on day 4 for IFA. Data are mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments; the results are expressed relative to the full control, defined as 100%. N.S., not significant. (Scale bar: 5 µm.)