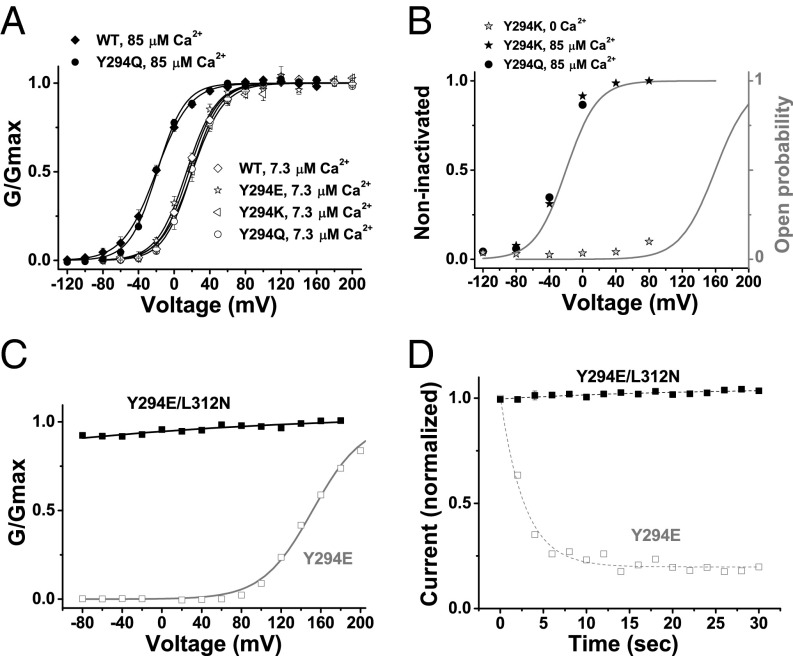
Fig. 3.
Closed-state dependence of inactivation in mutant BK channels. (A) Voltage dependence of BK channel activation for WT and Y294 mutants at 7.3 or 85 μM [Ca2+]i under symmetric K+ recording conditions. The gating parameters V1/2 and z obtained from single Boltzmann function fit at 7.3 μM Ca2+ are 17 ± 2 mV and 1.64 ± 0.07 e (n = 4) for WT, 14 ± 2 mV and 1.56 ± 0.15 e (n = 4) for Y294E, 20 ± 3 mV and 1.54 ± 0.14 e (n = 6) for Y294K, and 20 ± 3 mV and 1.70 ± 0.09 e (n = 6) for Y294Q. The V1/2 and z at 85 μM are −20 ± 2 mV and 1.43 ± 0.19 e (n = 4) for WT and 19 ± 1 mV and 1.66 ± 0.09 e (n = 4) for Y294Q. Error bars represent ±SEM. (B) Relationship between holding membrane voltages and availability of channels for quick activation (noninactivated channels) in Y294Q- and Y294K-mutant channels in the absence and presence of [Ca2+]i. Voltage dependence of channel open probability at 0 and 85 μM [Ca2+]i is included to show state dependence of inactivation. The gray curves are estimated voltage dependence of the channel’s open probabilities at 0 and 85 μM Ca2+ based on those measured at the symmetric K+ recording condition. (C) Relationship between normalized conductance (G/Gmax) and voltages for Y294E (gray) single-mutant and Y294E/L312N double-mutant (black) channels in the virtual absence of [Ca2+]i. (D) Time courses of available currents upon brief membrane depolarization in Y294E-mutant (gray) and Y294E/L312N-mutant (black) channels. The excised patches were held at −80 mV in the virtual absence of [Ca2+]i.