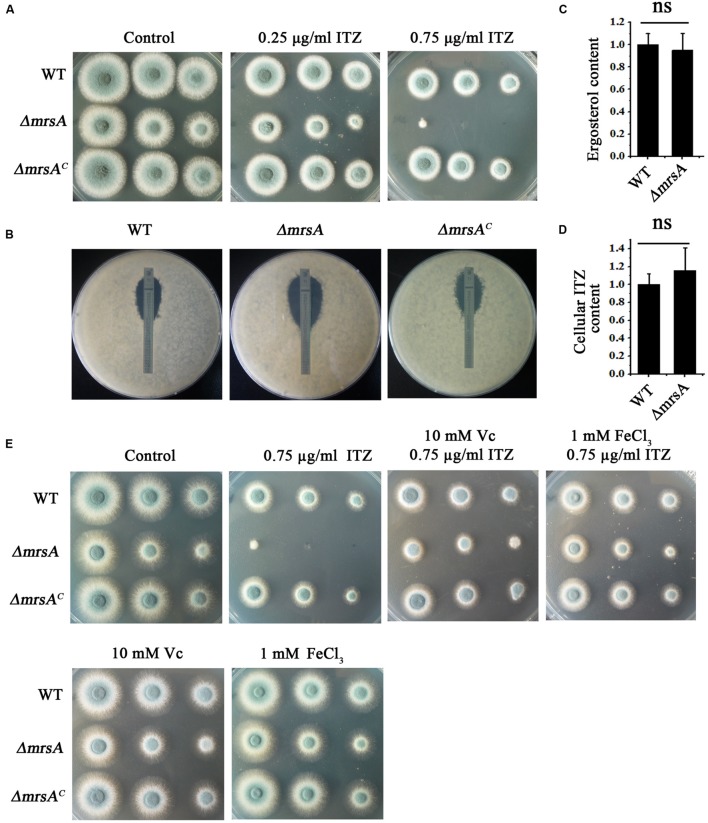
FIGURE 4.
ΔmrsA shows increased susceptibility to the antifungal drug itraconazole (ITZ). (A) Two microliters of DDW containing 104, 103, or 102 conidia of each strain were used to inoculate YAG medium containing 0.25 or 0.75 μg ml-1 ITZ. Colony growth was compared to that obtained on YAG containing no drugs. (B) For each strain, 1 × 105 conidia were mixed in YAG, and E-test strips of ITZ were placed on the plates. The MIC of ΔmrsA (0.38 μg ml-1) was significantly lower than that of the wild-type (1.0 μg ml-1) and ΔmrsAC (1.2 μg ml-1) strains. (C,D) Ergosterol production and intracellular ITZ accumulation of the parental wild-type strain and ΔmrsA were quantified using HPLC. Ergosterol and ITZ content of ΔmrsA was normalized to the level found in the parental strain (wild type = 1). (E) Serially diluted suspensions of conidia of each strain were spotted onto YAG plates containing the ROS scavenger L-ascorbic acid sodium (Vc, 10 mM) and/or ITZ (0.75 μg ml-1) and FeCl3 (1 mM).