Figure 6. miR-30 targets HNF4γ, whereas miR-194 targets NR2F2.
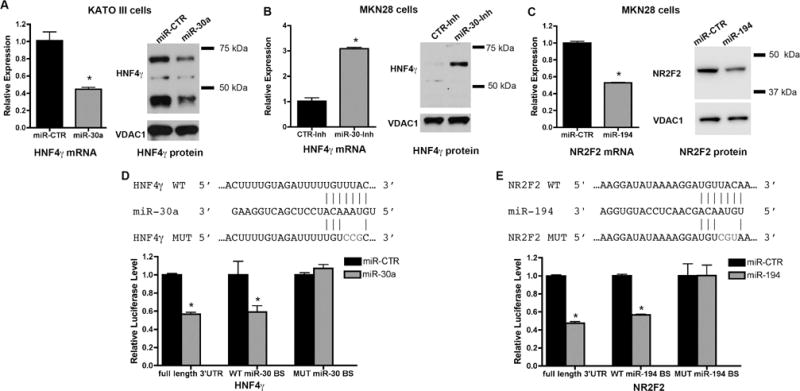
Cells were transfected with a miR-30a mimic (A), a miR-30 family inhibitor (B) or a miR-194 mimic (C), and at 96 hours after transfection, cells were processed for RNA extraction and qRT-PCR for analysis of HNF4γ and NR2F2 message levels or for Western blot for detection of HNF4γ and NR2F2 protein. HNF4γ protein bands in the miR-30 treated samples showed an average reduction of 40% in comparison with the miR-CTR treated samples (with p > 0.001, by Student’s t-test). NR2F2 protein band in the miR-194 treated samples showed an average reduction of 30% in comparison with the miR-CTR treated samples (with p = 0.003, by Student’s t-test). (D,E) Luciferase reporter assays showing the effect of miR-30a (D) or miR-194 (E) on the full-length 3′UTR and on the wild type (WT) miR binding site (BS), but not on the mutant (MUT) sequences within the 3′UTR regions of HNF4g (D) and NR2F2 (E). qRT-PCR analysis of indicated intestinal metaplasia markers after transfection of KATO III cells with either a miR-30 mimic or an siRNA against HNF4γ. All values are shown as means ± SD. Pairwise comparisons (miR-mimics vs. miR-CTR) were performed by Student’s t-test (* indicates P < 0.05).
