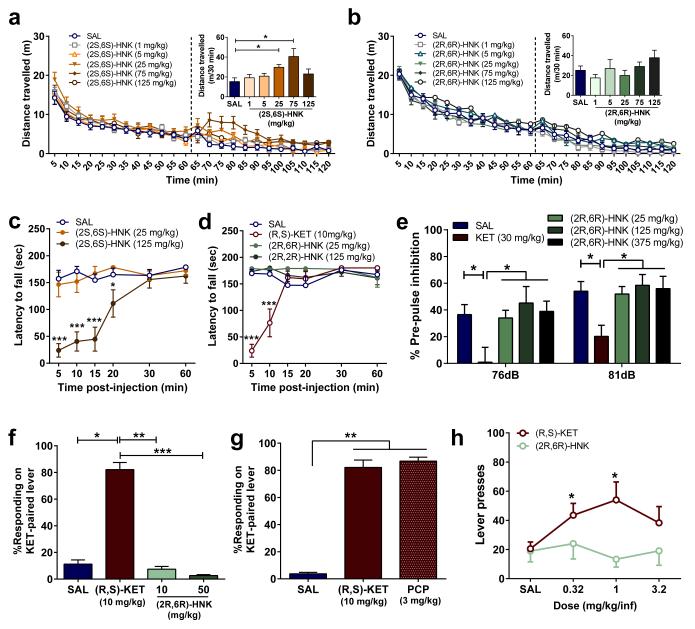
Figure 5. (2R,6R)-HNK lacks ketamine-related side effects.
(a,b) After recording baseline activity for 1 hour, mice received drug (dashed line) and locomotor activity was monitored for 1 hour. a, Administration of (2S,6S)-hydroxynorketamine (HNK) dose-dependently changed locomotor activity, while administration of b, (2R,6R)-HNK did not. c, (2S,6S)-HNK, but not d, (2R,6R)-HNK, induced motor in-coordination in the rotarod. Unlike (R,S)-KET, (2R,6R)-HNK administration did not induce e, pre-pulse inhibition deficits, (f,g), (R,S)-KET-associated discriminative stimulus, or h, self-administration. Data are means ± S.E.M. *p<0.05, **, p<0.01, ***p<0.001, KET vs saline (SAL); for panel c, * (R,S)-KET, # (2S,6S)-HNK (statistical analyses and n numbers see Supplementary Information Table 1).