Figure 4.
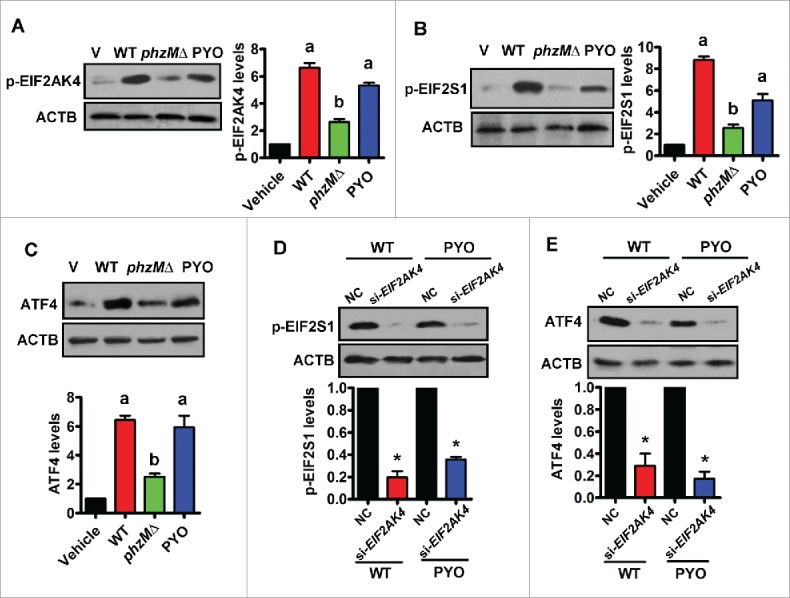
Pyocyanin activates the EIF2AK4-EIF2S1-ATF4 pathway in Beas-2B cells. (A and B) Beas-2B bronchial epithelial cells were infected with wild-type (WT) P. aeruginosa PA14, or the phzMΔ mutant, or treated with pyocyanin (PYO, 0.1 mM) for 8 h. The phosphorylation (p-) levels of EIF2AK4 (A) and EIF2S1 (B) were determined by western blotting. The blot is representative of 3 experiments. The right panels show quantification of phosphorylated EIF2AK4 or EIF2S1. All results are standardized to ACTB. a, P < 0.05 vs. vehicle (V); b, P < 0.05 vs. WT. (C) The protein levels of ATF4 were determined by western blotting. The lower panel shows quantification of ATF4. a, P < 0.05 vs. vehicle (V); b, P < 0.05 vs. WT. (D and E) Knockdown of EIF2AK4 by RNAi inhibited protein levels of phosphorylated EIF2S1 (D) and ATF4 (E) in Beas-2B cells infected with WT PA14 or treated by PYO. The lower panels show quantification of proteins. *, P < 0.05 vs. negative control (NC).
