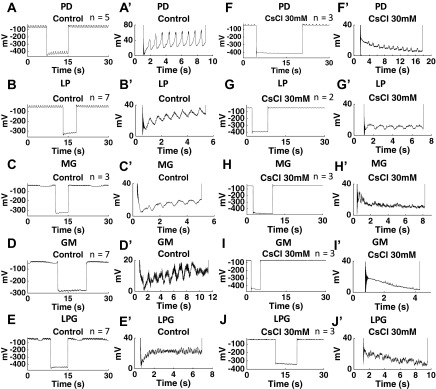
Fig. 2.
CsCl (30 mM) eliminated the voltage “sag” induced by hyperpolarization-activated inward cationic current (Ih) in the PD, LP, MG, GM, and LP neurons. A′, B′, C′, D′, E′, F′, G′, H′, I′, and J′ are magnified images from A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, and J, respectively. A, A′, B, B′, C, C′, D, D′, E, E′: in the control condition, the PD, LP, MG, GM and LPG neurons all showed voltage sag after a −10-nA hyperpolarization. F, F′, G, G′, H, H′, I, I′, J, J′: after application of 30 mM CsCl, the PD, LP, MG, GM, and LPG neurons did not show voltage sag after a −10-nA hyperpolarization. n Values are indicated in each plot. The large negative voltage value during hyperpolarization (A-J) was due to the unbalanced bridge when using the single microelectrode recording. Balancing the bridge is an adjustment of the output signal; it has no effect on the cells.