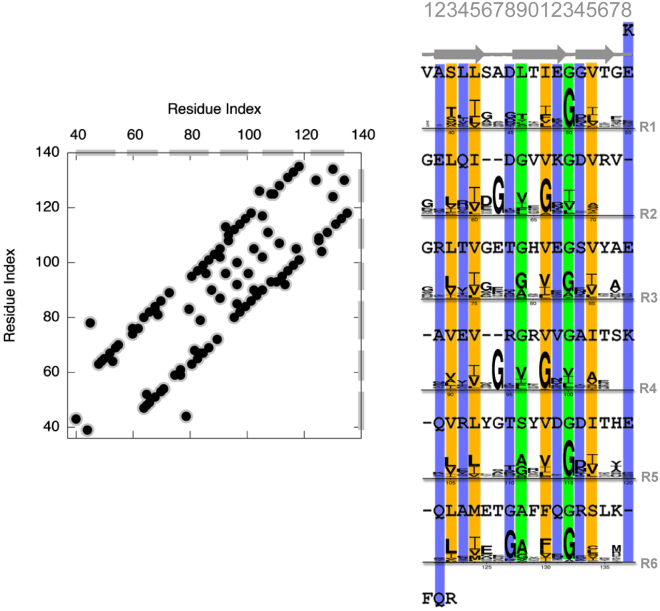
Figure 1.
Contact prediction and amino acid sequence of the bactofilin DUF583 domain. Left: the 50 top-scoring amino acid contacts obtained from a covariation analysis of an MSA using Gremlin. The gray bars on the axes represent the six internal repeats. Right: the amino acid sequence of the DUF583 domain has six internal repeats (R1–R6) that we aligned using the structure we determined. Gaps are added where neighboring repeats bulge to maintain the phase. Between the repeats, we show sequence logos that represent the conservation pattern in the MSA of the bactofilin domains. The individual columns are color-coded depending on the kind of amino acids that are dominant, with orange (columns 3, 5, 11, and 15) representing mostly hydrophobic amino acids and blue (columns 2, 4, 8, 12, and 14) representing hydrophilic and charged amino acids. Two columns that contain many glycine residues are shown in green (columns 9 and 13) and are located in the loops that connect the different strands. To see this figure in color, go online.