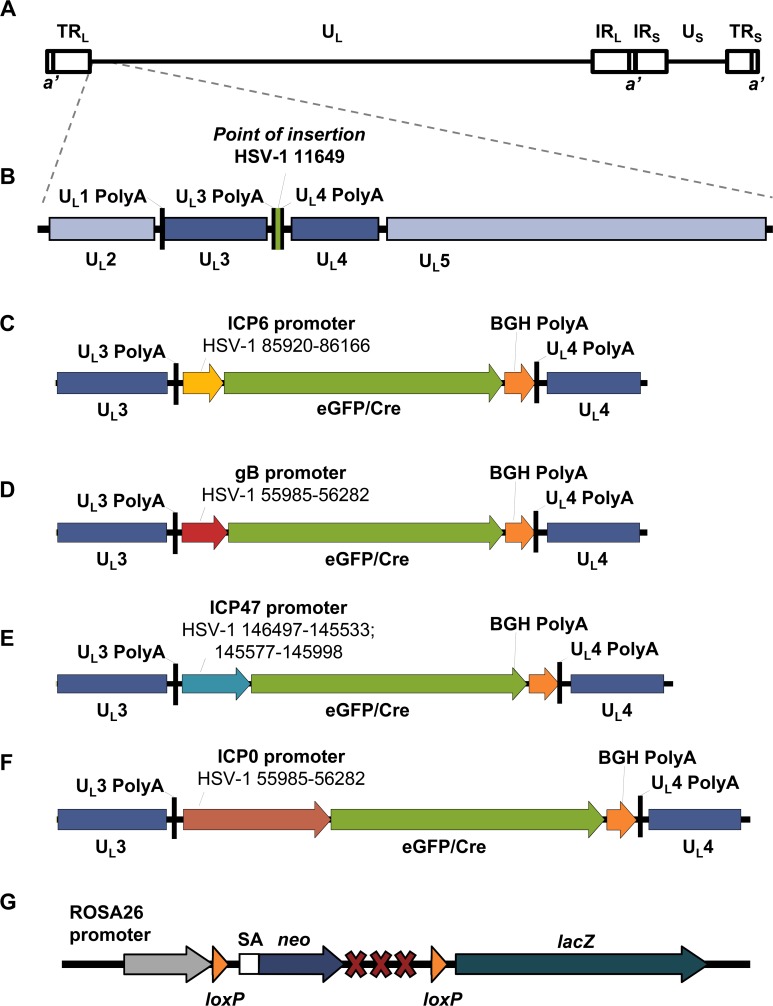
Fig 1. Design of HSV-1 viruses that express eGFP/Cre.
(A) Schematic representation of the HSV-1 genome (to scale). (B) Schematic representation of the UL3/UL4 intergenic region, with the position at which the eGFP/Cre cassette is inserted indicated in green, and the base pair position indicated using coordinates from the HSV-1 KOS genome (JQ673480). Schematic representation of the eGFP/Cre gene under the control of the (C) ICP6 promoter, (D) gB promoter, (E) ICP47 promoter or (F) ICP0 promoter inserted into the HSV-1 genome, with the sequences of the promoter indicated based on HSV-1 KOS genome coordinates. (G) Schematic representation of the ROSA26 locus of ROSA26 mice. A splice acceptor sequence (SA) is located upstream of a neomycin gene (neo) followed by a triple polyadenylation site, all of which is flanked by loxP sites. The ROSA26 promoter is located upstream of this transgene, while the lacZ gene is located downstream. Following Cre-mediated recombination, the neo transgene is removed and lacZ is constitutively expressed from the ROSA26 promoter.