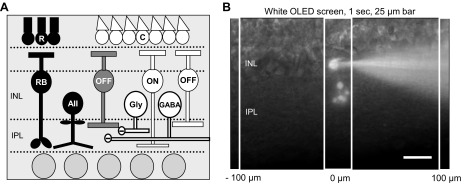
Fig. 1.
OFF bipolar cell inhibition. A: schematic of OFF bipolar cell inhibitory input pathways. Rod photoreceptors (R) activated by dim light release glutamate onto rod bipolar cells (RB), which release glutamate onto AII amacrine cells (AII). AII amacrine cells release glycine onto OFF cone bipolar cells (OFF; black pathway). Cone photoreceptors (C) are activated by brighter light and release glutamate onto OFF and ON cone (ON) bipolar cells. Activation of these bipolar cells in turn releases glutamate onto other wide-field GABAergic (GABA) and narrow-field glycinergic (Gly) amacrine cells, which also have inputs onto OFF bipolar cells (white pathways). INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer. B: diagram of experimental protocol. Example cell morphology of an Alexa 488-filled OFF type 3 bipolar cell in a retinal slice preparation. To examine spatial inhibitory input to OFF bipolar cells, 25-μm bars of white light were presented to the retinal slice for 1 s, as shown, using a white OLED screen mounted on the microscope. Bars of light were presented every 100 μm from the recorded cell, extending in both directions, with 30 s between stimuli. Scale bar, 25 μm.