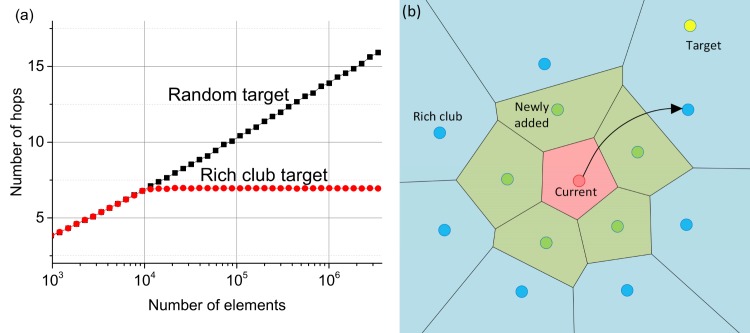
Fig 4.
(a) Average number of greedy algorithm hops scaling for the first 104 elements given as start and target nodes (red) and all elements used for search (black). The first 104 elements form a rich club that ignores more newly added elements. The results are presented for Euclidian data with d = 2, M = 20. (b) Cartoon of Voronoi partition for connections of a single greedy search step. Newly added elements (green) cause only local changes in Voronoi partitioning, so if the target element lies outside the current element connections, it falls into Voronoi partition of rich club’s elements (blue), thus ignoring local connections at greedy search.