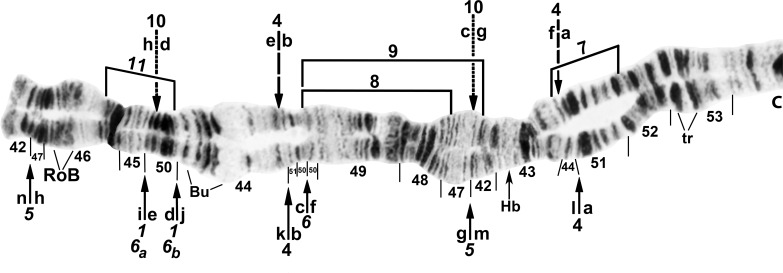
Fig 5. IIS arm of Simulium cholodkovskii (female larva), showing the typical sequence (IIS-1,4,5,6).
Limits of polymorphic inversions IIS-7–IIS-9 and IIS-11 are indicated by brackets; 6a and 6b denote alternative breakpoints for IIS-6. The standard sequence for the subgenus Simulium can be obtained from the IIS-1,4,5,6 sequence by alphabetically ordering the fragments indicated by small letters ‘a’ through ‘n’ that appear below the chromosome. Ordering the fragments above the chromosome from ‘a’ to ‘h’ produces the Y-chromosome sequence (IIS-1,5,6,10) of S. nigricoxum, i.e. IIS-10 is Y linked (dotted lines), whereas IIS-4 is X-linked (dashed lines) and, therefore, absent on the Y. Bu = bulge, C = centromere, Hb = location of heteroband 43Hb, RoB = ring of Balbiani, tr = trapezoidal.