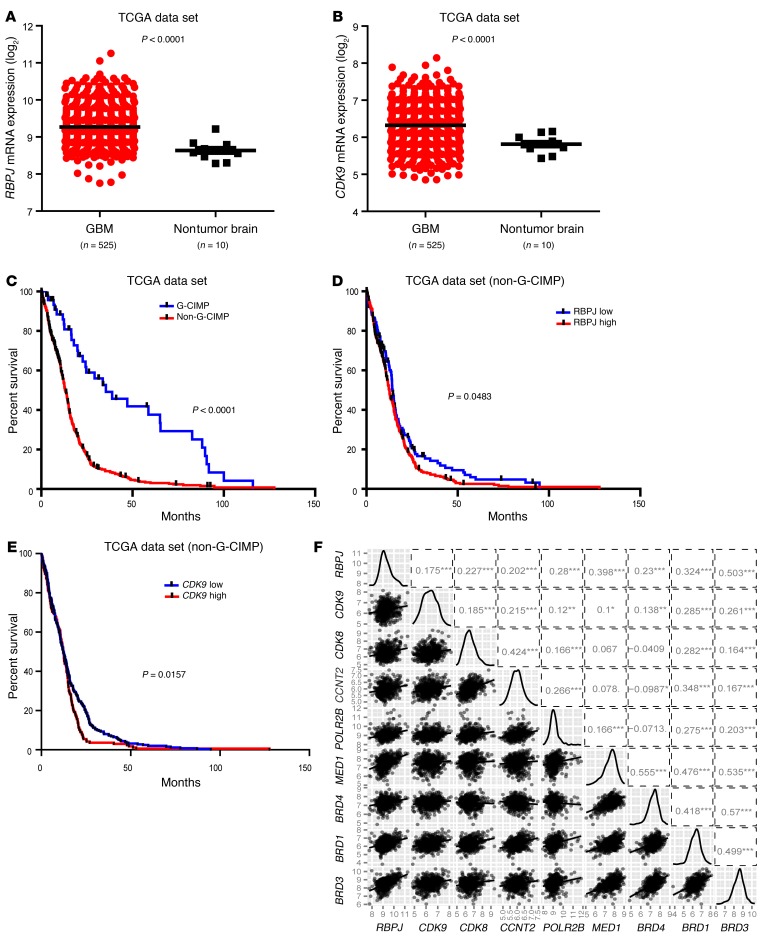
Figure 9. RBPJ and CDK9 regulation informs patient prognosis.
(A and B) Relative mRNA expression levels of (A) RBPJ and (B) CDK9 in nontumor brain and glioblastoma were determined in TCGA data set. (C) Analysis of TCGA data indicates that non–G-CIMP glioblastoma (GBM) patients have much poorer survival (P < 0.0001 by log-rank analysis). (D) Analysis of TCGA data indicates that higher RBPJ mRNA expression informs poor prognosis of non–G-CIMP patients (P = 0.0483 by log-rank analysis). (E) Analysis of TCGA data indicates that higher CDK9 mRNA expression informs poor prognosis of non–G-CIMP patients (P = 0.0157 by log-rank analysis). (F) Pairwise correlation analysis of RBPJ and transcriptional elongation–related genes was performed in the TCGA glioblastoma data set. Plots indicate expression data from TCGA patients for indicated genes, and numbers represent correlation coefficient (r) values.