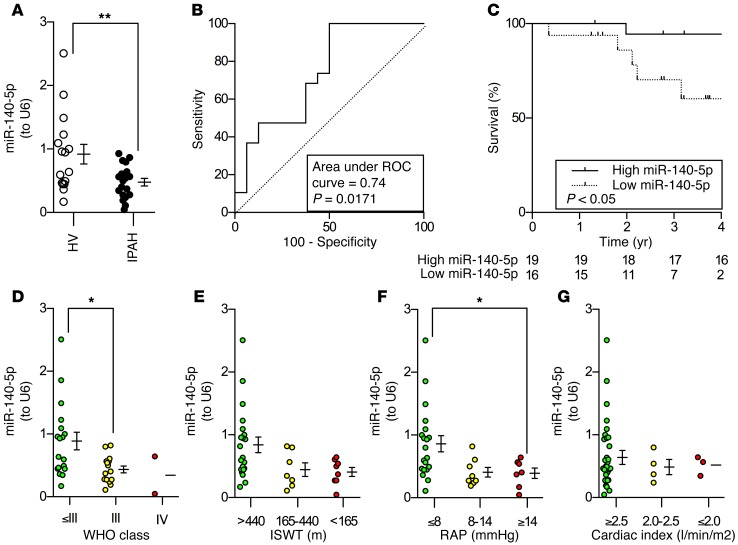
Figure 2. miR-140-5p is reduced in patients with IPAH.
(A) Lower whole blood levels of miR-140-5p were observed in patients with IPAH when compared with HV (IPAH, n = 20, HV, n = 16, **P < 0.01, unpaired 2-tailed Student’s t test, mean ± SEM). (B) Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve showing sensitivity and specificity of whole blood miR-140-5p levels for discriminating patients with PAH from HV at time of diagnosis (IPAH, n = 20, HV, n = 16, area under ROC curve = 0.74, P = 0.0171). (C) Kaplan-Meier analysis of survival, stratified by ROC-derived miR-140-5p cut-off. Survival in patients with miR-140-5p levels above the cut-off is indicated by the solid line and survival in patients with levels below by the dashed line. The table beneath the graph indicates numbers at risk over time in years (IPAH, n = 20, HV, n = 16, *P < 0.05, log-rank [Mantel-Cox] test). (D–G) Reduced levels of miR-140-5p are present in patients with increasing clinical severity of PAH: WHO class (D), incremental shuttle walk test distance (ISWT) (E), right atrial pressure (RAP) (F), and cardiac index (G) (D–G: IPAH, n = 20, HV, n = 16, *P < 0.05, 1-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test correction, mean ± SEM).