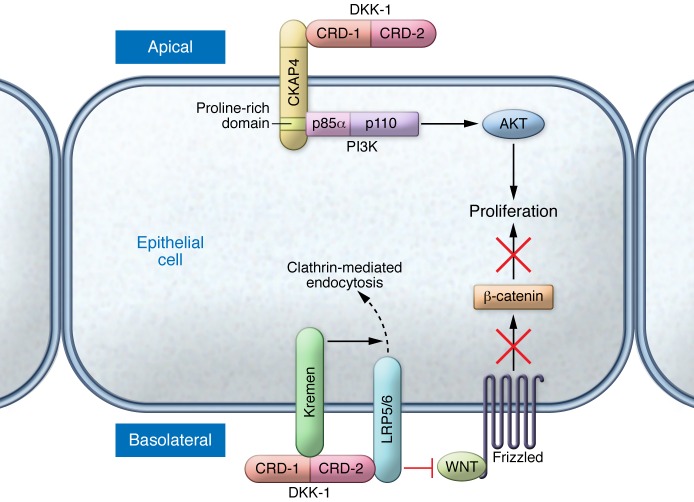
Figure 1. DKK-1 stimulates proliferation by binding to CKAP4 and activating AKT.
DKK-1 is secreted from epithelial cells and binds to the extracellular domain of CKAP4 at the apical surface of the cell. The CRD-1 of DKK-1 and the leucine zipper (LZ) domain of CKAP4 are required for this interaction (although a direct interaction between the two has not yet been shown). Upon DKK-1 binding, CKAP4 binds to the p85α subunit of PI3K to activate PI3K/AKT signaling and stimulate cancer cell proliferation. This signaling motif is in contrast to the well-established role for DKK-1 as a canonical Wnt antagonist, in which CRD-2 of DKK-1 binds to the Wnt coreceptor LRP5/6 (preventing interaction with Wnts) and to Kremen (driving internalization of LRP5/6).