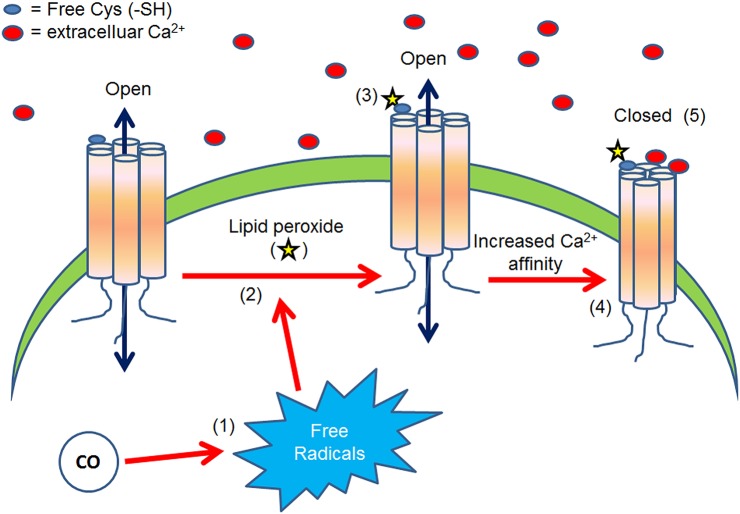
Figure 1.
The above diagram presents what is proposed as a possible molecular mechanism to explain the CO-induced Cx46 inhibition. CO increases free radicals concentration (1) which in turn induces lipid peroxide production (2). Then, lipid peroxides can induce the carbonylation of extracellular cysteine (-SH) (3), increasing Cx46-Ca2+ sensitivity (4) and thus stabilizing the closed state of the loop gating (5).