Figure 4.
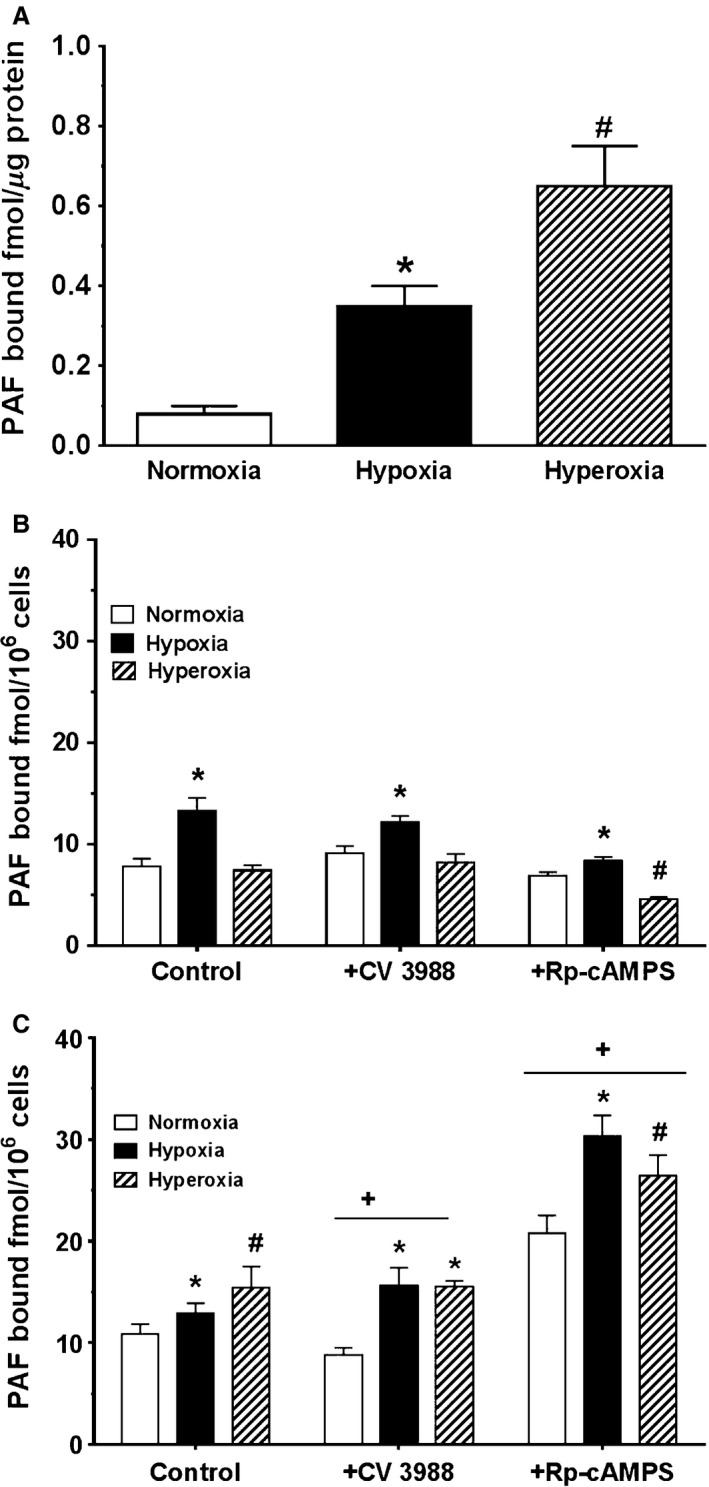
A, Baseline effect of normoxia, hypoxia, and hyperoxia on platelet‐activating factor (PAF) receptor binding in newborn pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMC) membrane proteins. Membrane proteins were isolated from cells cultured for 24 h in normoxia, hypoxia, or hyperoxia and subject to 3H‐PAF ligand binding as described in methods. Data are mean ± SEM, n = 4 for each oxygen tensions. PAF binding in normoxia was 0.08 fmol/microgram of membrane protein. Hypoxia increased binding over fourfold more than normoxia, and hyperoxia increased binding eightfold more than normoxia. *p < 0.05, different from normoxia, # P < 0.05, different from normoxia or hypoxia. B, Effect of acute exposure to oxygen tension on PAFR binding to adherent newborn PASMC. Adherent newborn PASMC were preincubated for 4 h in normoxia, hypoxia, and hyperoxia, then subjected to 3H‐PAF ligand binding as described in methods. Data are mean ± SEM, n = 4 for each oxygen tensions. Baseline‐specific PAF receptor binding to adherent cells following 4 h incubation in normoxia was 7.85 ± 0.77 fmol/106cells. Hypoxia augmented specific PAF receptor binding by 70% but no significant difference was demonstrated following 4 h incubation in hyperoxia. *P < 0.05, different from normoxia, # P < 0.05, different from normoxia or hypoxia. C, Effect of prolonged exposure to different oxygen tension on PAF receptor binding to newborn PASMC. Adherent newborn PASMC were cultured for 72 h in normoxia, hypoxia, and hyperoxia, then subjected to 3H‐PAF ligand binding as described in methods. Data are mean ± SEM, n = 4 for each oxygen tension. In general, prolonged hypoxia or hyperoxia increased PAFR binding to adherent cells. Incubation for 72 h in hypoxia produced a 19% increase in binding in comparison with normoxia. Incubation in 72 h of hyperoxia amplified binding by over 40% compared to 72 h of normoxia. Pretreatment with CV3988 decreased binding in normoxia but increased binding in hypoxia in comparison with controls. Pretreatment with Rp‐cAMPS significantly increased specific PAFR binding in all three oxygen conditions, a twofold increase in binding in normoxia, 1.5‐fold increase in binding in hypoxia, and 70% increase in binding in hyperoxia. *P < 0.05, different from normoxia; # P < 0.05, different from normoxia or hypoxia; + P < 0.05, different from control and CV3988 conditions.
