Abstract
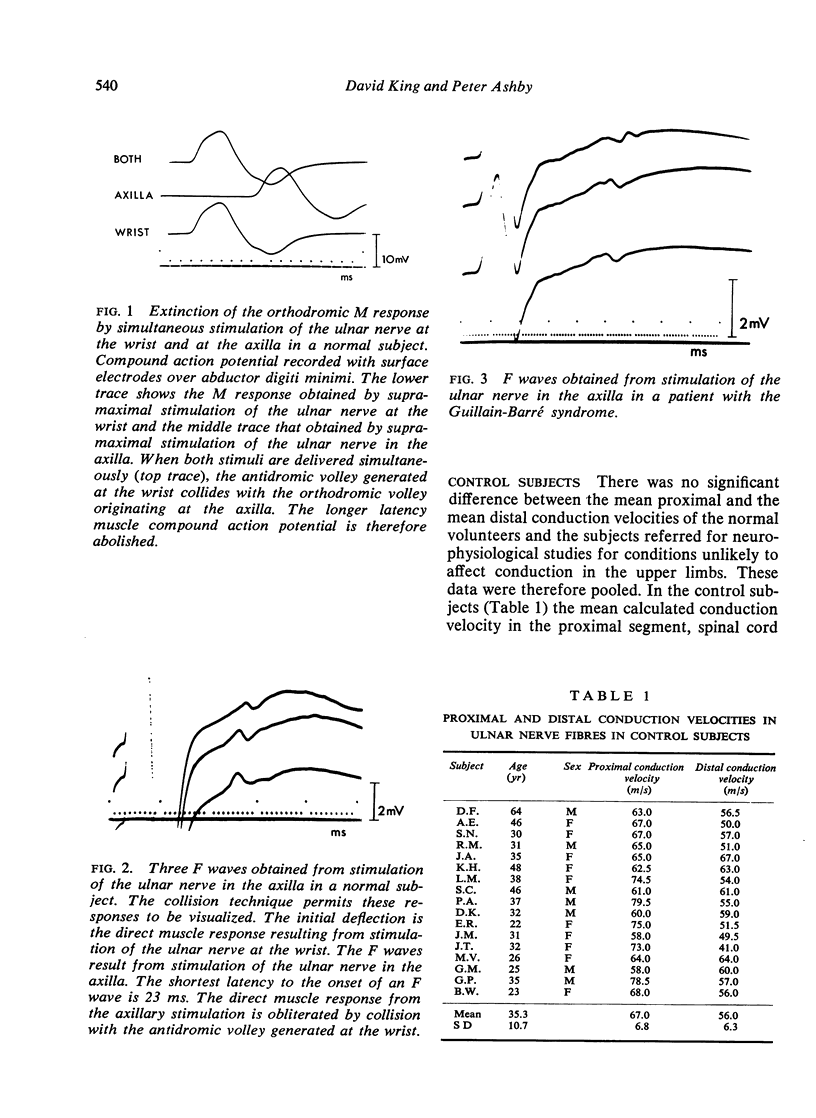
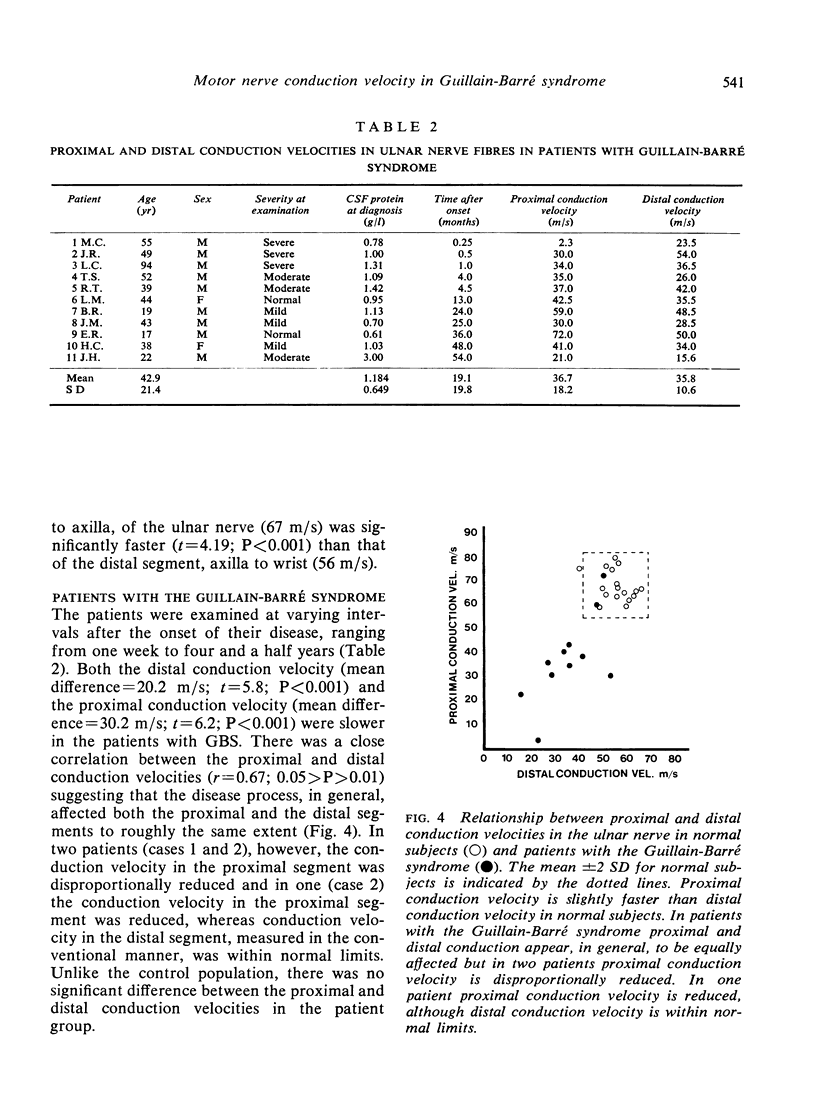
Conduction velocity from spinal cord to axilla (estimated using the F wave) has been compared with conduction velocity from axilla to wrist (measured in the conventional manner) in the motor fibres of the ulnar nerve in 17 controls subjects and in 11 patients with the Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS). In the patients with GBS the conduction velocity was, in general reduced to a similar extent in both the proximal and the distal portions of the motor fibres, suggesting that the disease process is usually diffuse. In two patients, however, the conduction velocity in the proximal segment was disproportionally reduced and in one of these the conduction velocity in the distal segment was normal. It is concluded that the estimation of conduction velocity in the proximal segments of motor nerves may be of value in the assessment of patients with GBS.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asbury A. K., Arnason B. G., Adams R. D. The inflammatory lesion in idiopathic polyneuritis. Its role in pathogenesis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1969 May;48(3):173–215. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196905000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigot P., Goulon M. Evolution of electrological data in polyradiculitis. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1970 Nov;29(5):534–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CERRA D., JOHNSON E. W. Motor nerve conduction velocity in "idiopathic" polyneuritis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1961 Mar;42:159–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter S. An ultrastructural study of an acute fatal case of the Guillain-Barré syndrome. J Neurol Sci. 1972 Feb;15(2):125–140. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(72)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jesus P. V., Jr Landry-Guillian-Barre-Strohl syndrome: neuronal disorder and clinico-electrophysiological correlation. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1974 Mar-May;14(2):115–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen A., Humphreys P. The Guillain-Barré syndrome. A clinical and electrodiagnostic study of 25 cases. Arch Neurol. 1974 Jun;30(6):438–443. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490360014004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINEAN J. B., WOOLF A. L. An electron microscope study of degenerative changes in human cutaneous nerve. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1962 Jan;21:105–115. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196201000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feasby T. E., Brown W. F. Variation of motor unit size in the human extensor digitorum brevis and thenar muscles. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Aug;37(8):916–926. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.8.916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fra L., Brignolio F. F and H responses elicited from muscles of the lower limb in normal subjects. J Neurol Sci. 1968 Sep-Oct;7(2):251–261. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(68)90147-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGBARTH K. E. Post-tetanic potentiation of myotatic reflexes in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1962 Feb;25:1–10. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.25.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isch F., Isch-Treussard C., Jesel M. Valeur diagnostique et pronostique des données électromyographiques dans les polyradiculonévrites. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1967 Jul;117(1):21–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J., Butzer J. F. F-wave conduction velocity in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Assessment of nerve segment between axilla and spinal cord. Arch Neurol. 1975 Aug;32(8):524–529. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490500044004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J. F-wave velocity in the central segment of the median and ulnar nerves. A study in normal subjects and in patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Neurology. 1974 Jun;24(6):539–546. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.6.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAFRATTA C. W., SMITH O. H. A STUDY OF THE RELATIONSHIP OF MOTOR NERVE CONDUCTION VELOCITY IN THE ADULT TO AGE, SEX, AND HANDEDNESS. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1964 Aug;45:407–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGLADERY J. W., McDOUGAL D. B., Jr Electrophysiological studies of nerve and reflex activity in normal man. I. Identification of certain reflexes in the electromyogram and the conduction velocity of peripheral nerve fibers. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1950 May;86(5):265–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer R. F., Feldman R. G. Observations on the nature of the F wave in man. Neurology. 1967 Feb;17(2):147–156. doi: 10.1212/wnl.17.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod J. G., Wray S. H. An experimental study of the F wave in the baboon. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1966 Jun;29(3):196–200. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.29.3.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQuillen M. P. Idiopathic polyneuritis: serial studies of nerve and immune functions. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971 Oct;34(5):607–615. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.34.5.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer D. R., Spalding J. M. Late residua of acute idiopathic polyneuritis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1973 Dec;36(6):978–988. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.36.6.978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleasure D. E., Lovelace R. E., Duvoisin R. C. The prognosis of acute polyradiculoneuritis. Neurology. 1968 Dec;18(12):1143–1148. doi: 10.1212/wnl.18.12.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawnhey B. B., Kayan A. A study of the F wave from the facial muscles. Electromyography. 1970 Sep-Oct;10(3):287–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne J. Central responses to electrical activation of the peripheral nerves supplying the intrinsic hand muscles. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1965 Dec;28(6):482–495. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.28.6.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trontelj J. V., Trontelj M. F-responses of human facial muscles. A single motoneurone study. J Neurol Sci. 1973 Oct;20(2):211–222. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(73)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton A. R., McComas A. J., Sica R. E. Potentiation of "late" responses evoked in muscles during effort. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971 Dec;34(6):699–711. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.34.6.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski H., Terry R. D., Whitaker J. N., Cook S. D., Dowling P. C. Landry-Guillain-Barré syndrome. A primary demyelinating disease. Arch Neurol. 1969 Sep;21(3):269–276. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480150059008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


