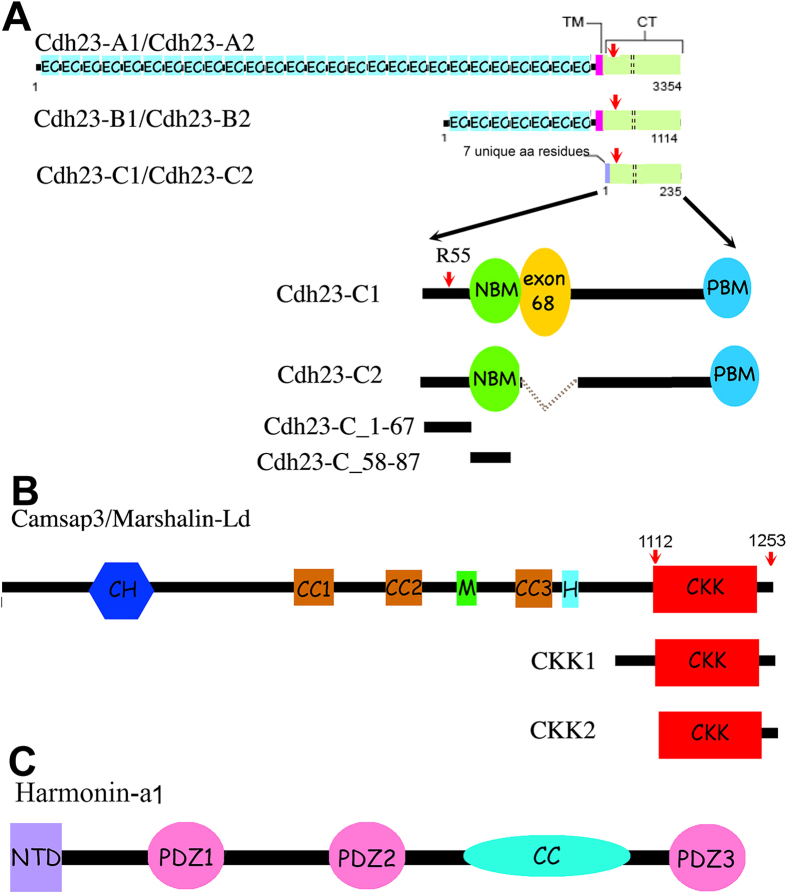
Figure 1. A schematic representation of domain organization and corresponding cDNA constructs of mouse CDH23 isoforms, CAMSAP3/Marshalin-Ld, and harmonin-a1.
(Panel A) Three CDH23 isoforms and their subtypes. Cdh23 undergoes alternative splicing that involves the inclusion (subtype 1) or exclusion (subtype 2) of exon 68 (shown as an orange circle in CDH23-C1 or as dotted lines for CDH23-C2), which encodes 35 cytoplasmic amino acids. CDH23-A consists of 27 extracellular cadherin (EC) repeats, a transmembrane (TM) domain (pink box), and a cytoplasmic domain (CT, pale green box), which contains PDZ-binding Motifs (PBM), and the N-terminal domain of a harmonin binding motif (NBM) (details shown in CDH23-C1). The B isoform proteins differ from CDH23-A in that they have seven EC motifs. The C isoforms are cytosolic and do not have EC repeats or the TM. C1 and C2 both have seven novel amino acids coded by exonic sequences in the N-terminus. The red arrow indicates the R3175H position in the CT, and the corresponding mutation at R55 in mouse Cdh23-C. (Panel B) CAMSAP3/Marshalin-Ld and the CKK domain constructs. CAMSAP3, also called Marshalin-Ld21, codes three CC (coiled-coil) domains (brown), CKK (a carboxy-terminal tubulin-binding) domain (red), the CH (calponin homology) domain (blue), a microtubule-binding (M) domain (green), and a helical (H) domain (light blue). Although CKK1 (resides 1020–1253) and CKK2 (resides 1112–1253) both contain the CKK domain, CKK1 includes an extra region N-terminus to the CKK domain, and derived from CAMSAP3/Marshalin-Ld. (Panel C) Harmonin-a1. Harmonin-a1 contains the N-terminal domain (NTD) (purple), three PDZ (PSD-95/Dlg/ZO-1) domains (pink), and a predicted CC domain (turquoise).