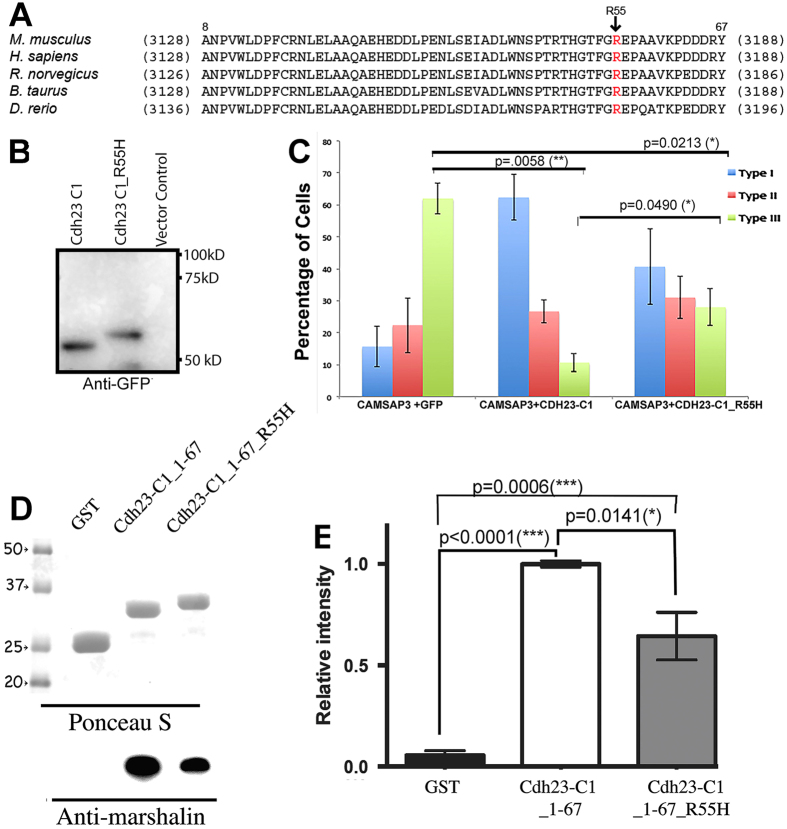
Figure 7. Mutation in the CBM decreases CDH23-C’s ability to bind CKK.
(A) The R3175 site resides in the CBM, a highly conserved cytoplasmic region of CDH23. Amino acid sequences of CBM from mouse CDH23-A1 (NM023370) are aligned with corresponding sequences from four species (human, NM022124; Rat, BAB61904; Cattle, DAA14294; Zebrafish, AAS98176). Numbers in parentheses indicate residue numbers at the beginning and end of CBM. Residue numbers corresponding to mouse CDH23-C1 are indicated above the mouse CDH23-A1 sequence. Location of mutation R3175H is shown with an arrow. (B) Western Blot of CDH23-C1-GFP and CDH23-C1_R55H-GFP, detected by anti-GFP. Change from R to H significantly alters the apparent molecular weight of CDH23-C1_R55H, which is larger than CDH23-C1. (C) In vitro MT formation assay. A bar graph shows the distribution of three expression patterns (as in Fig. 3A) of CAMSAP3/Marshalin-Ld in OK cells 24 hours post transfection with plasmids encoding CAMSAP3/Marshalin-Ld and Cdh23-C1-GFP or Cdh23-C1_R55H-GFP, respectively. CDH23-C1_R55H reduces type III MT bundle formation to some degree, but less effectively than CDH23-C1 (p = 0.0490, n = 3, mean ± s.e.m.). (D,E) GST pull-down assays of CDH23-C1 fragments. Binding between Cdh23-C aa 1–67 with or without R3175H mutation (CDH23-C_1–67_R55H) and CKK is significantly different. Compared to the negative control (GST), both CDH23-C_1–67 and CDH23-C_1–67_R55H bind to CKK (p ≤ 0.0001 and p = 0.0006, respectively). However, the binding to CKK is consistently reduced in CDH23-C_1–67_R55H compared to WT (p = 0.0141, n = 4, mean ± s.e.m.). Molecular weights (in kD) are labeled with numbers and arrowheads.