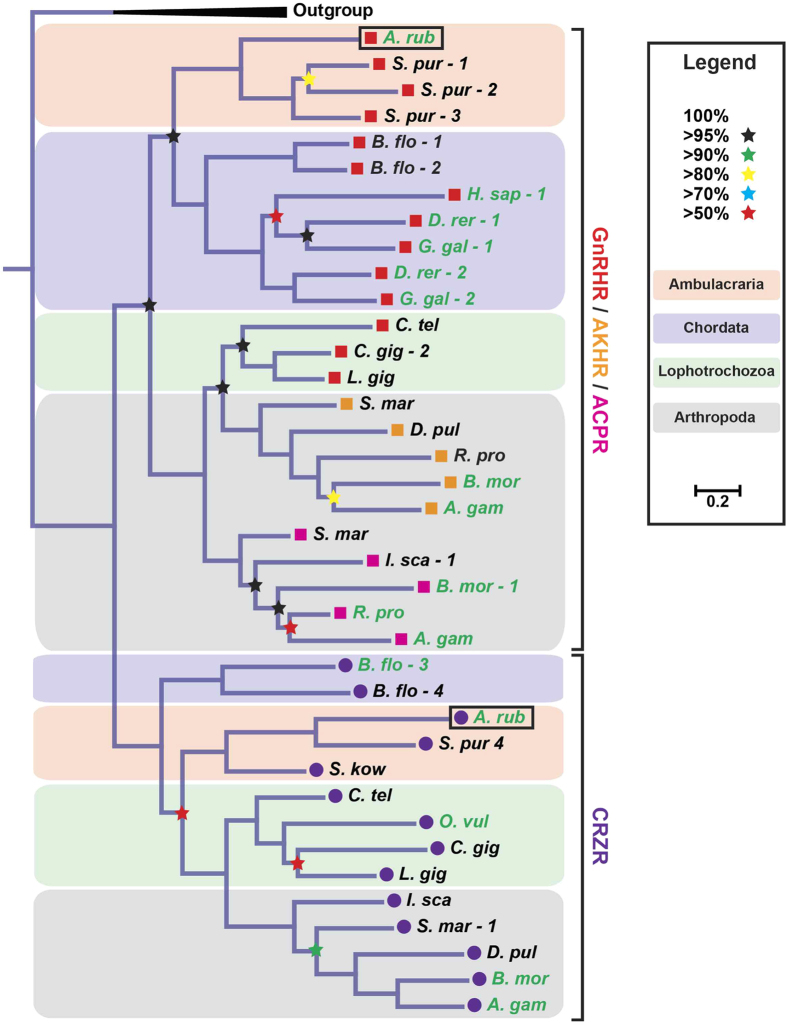
Figure 1. Phylogenetic analysis of GnRH/AKH/ACP/CRZ-type receptors using a Bayesian method reveals two distinct clades–a GnRH/AKH/ACP-type receptor clade and a CRZ-type receptor clade.
Single representatives of both clades are present in the starfish A. rubens (A. rub., black boxes). GnRH-type receptors are labelled using red squares, AKH-type receptors using orange squares, ACP-type receptors using pink squares and CRZ-type receptors using purple circles. Neuropeptide S and CCAP receptors were used as an outgroup (condensed). The stars represent posterior probabilities and the pastel coloured backgrounds represent different groups of animals (see legend). The scale bar indicates amino acid substitutions per site. Species for which receptor-ligand interactions have been experimentally characterized are coloured in green, including the A. rubens receptors characterized in this study (boxed). Species names are as follows: A. rub, Asterias rubens; S. pur, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus; B. flo, Branchiostoma floridae; H. sap, Homo sapiens; D. rer, Danio rerio; G. gal, Gallus gallus; C. tel, Capitella teleta, C. gig, Crassostrea gigas; L. gig, Lottia gigantea; S. mar, Strigamia maritima; D. pul, Daphnia pulex; B. mor, Bombyx mori; R. pro, Rhodnius prolixus; A. gam, Anopheles gambiae; I. sca, Ixodes scapularis; S. kow, Saccoglossus kowalevskii; O. vul, Octopus vulgaris. [accession numbers and references for the receptor sequences are included the legend of Supplementary Figure S3].