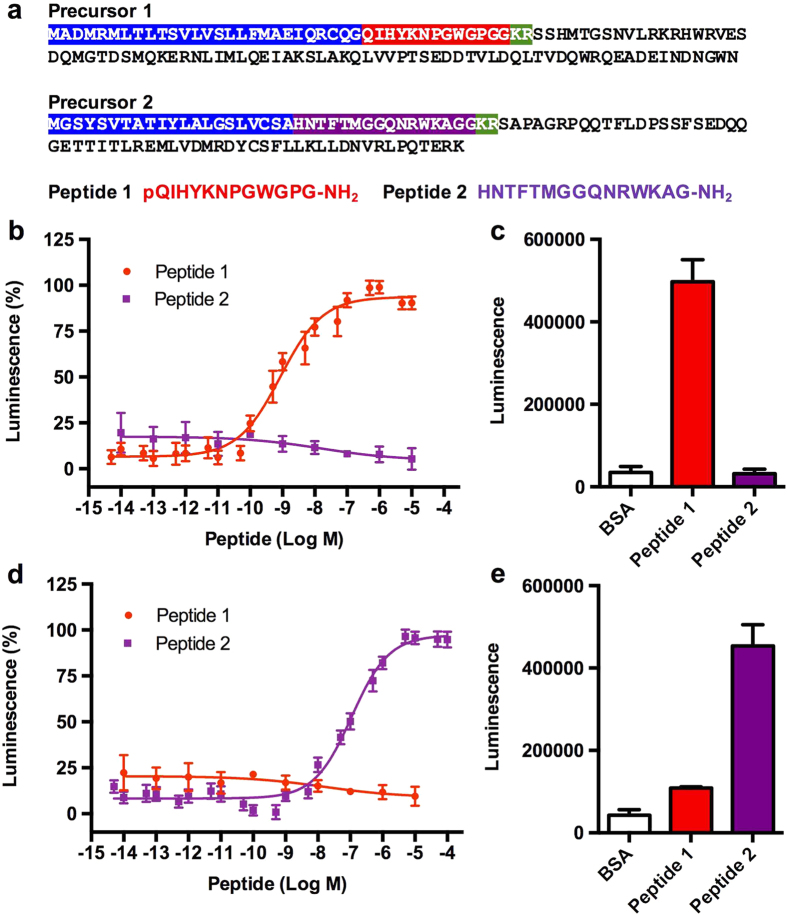
Figure 2. Identification of GnRH-type and Corazonin-type (CRZ)-type signalling systems in the starfish Asterias rubens.
(a) Amino acid sequences of two A. rubens GnRH/CRZ-type neuropeptide precursor proteins–precursor 1 and precursor 2. Signal peptides are highlighted in blue, putative neuropeptides (without post-translational modifications) are highlighted in red (peptide 1) or purple (peptide 2) and dibasic cleavage sites are highlighted in green. Peptides 1 and 2 with post-translational N-and C-terminal modifications, determined by mass spectrometry, are shown below the precursor sequences. (b) Peptide 1 causes dose-dependent stimulation of a bioluminescence response in CHO-K1 cells stably expressing aequorin and Gα16 and transfected with ArGnRHR; EC50 = 6.03 × 10−10 M. Peptide 2 has no effect when tested over the same concentration range as peptide 1, demonstrating the specificity of the activation of ArGnRHR by peptide 1, which is therefore designated as “ArGnRH”. (c) Comparison of the total bioluminescent responses of ArGnRHR-expressing cells for 30 seconds after the addition of BSA media (control), peptide 1 (10−5 M) or peptide 2 (10−5 M). (d) Peptide 2 causes dose-dependent stimulation of a bioluminescence response in CHO-K1 cells stably expressing aequorin and Gα16 and transfected with ArCRZR; EC50 = 1.15 × 10−7 M. Peptide 1 has no effect when tested over a similar concentration range as peptide 2, demonstrating the specificity of the activation of ArCRZR by peptide 2, which is therefore designated as “ArCRZ”. (e) Comparison of the total bioluminescent responses of ArCRZR-expressing cells for 30 seconds after the addition of BSA media (control), peptide 1 (10−5 M) or peptide 2 (10−5 M).