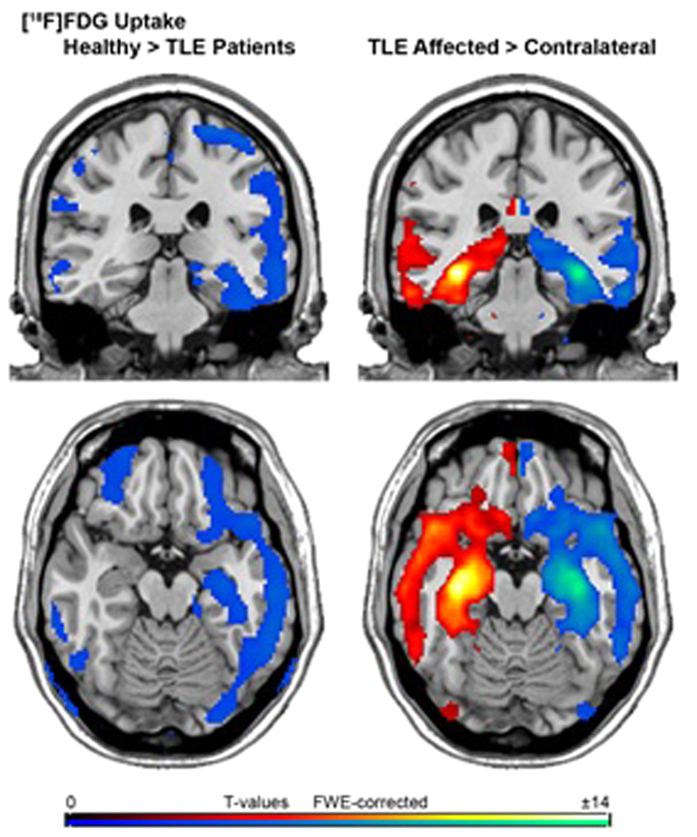
Figure 1. A coronal and transversal view of differences in FDG uptake between patients with TLE (patients with RTLE and LTLE pooled as one group) and the healthy control group (images on the left side) and between the affected and the contralateral hemisphere in all patients (RTLE and LTLE pooled together, images on the right side).
We found most pronounced decrease of FDG uptake in the temporal lobe including hippocampus of the affected hemisphere (AH) and otherwise spread throughout the entire cortex, except for the ant/middle cingulate cortex, in the AH and contralateral hemisphere (CH), when comparing patients with TLE to healthy controls. Furthermore, when comparing AH to CH in all patients pooled together, we detected a significant decrease in FDG uptake in the AH, including hippocampus, parahippocampus, inferior, medial and superior temporale lobe, temporal pole, fusiform gyrus, amygdala and the insula as well as thalamic, caudatus, anterior cingulate cortex, inferior orbitofrontal cortex and precuneus/posterior cingulum. The colour table shows the corresponding t-value (t > 5.7, P < 0.05; FWE-corrected at cluster level).