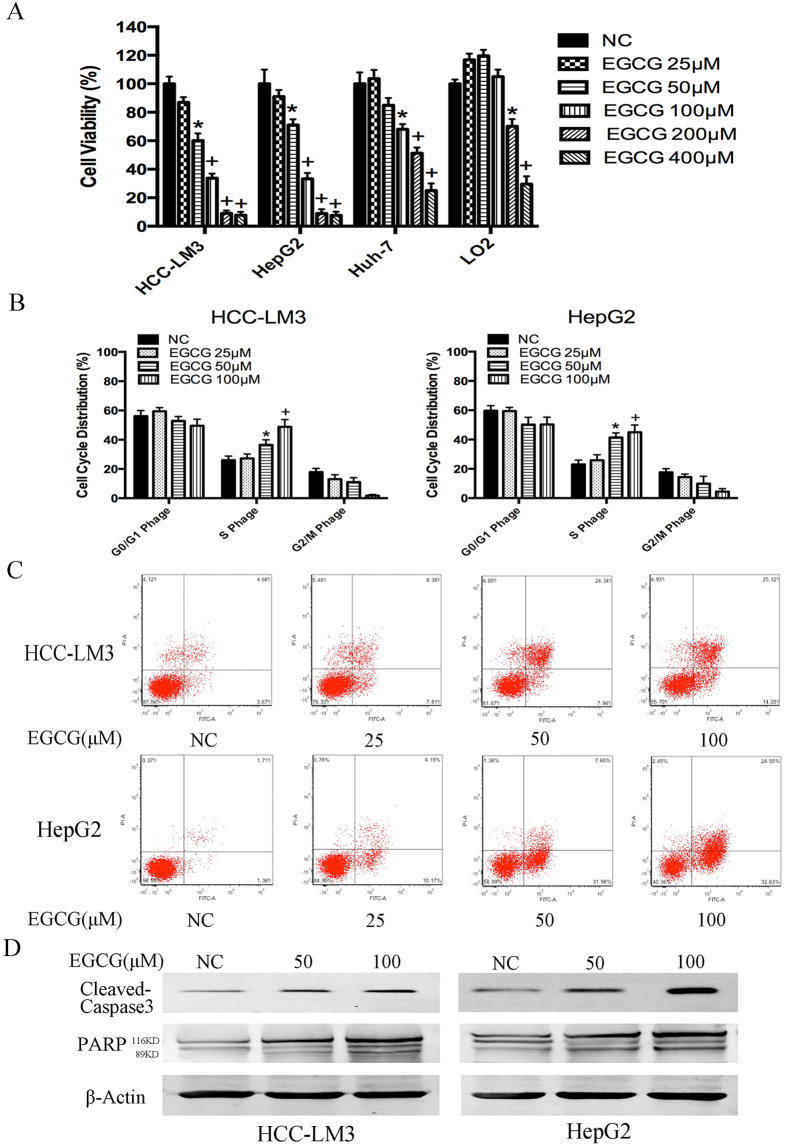
Figure 3. Effects of EGCG on HCC cell proliferation inhibition, S phage arrest, and apoptosis induction.
(A) HCC cells were cultured with or without EGCG (25, 50, 100, 200 and 400 μM) for 24 h and cell viability was examined using the CCK-8 method. (B) EGCG induced cell cycle arrest in HCC-LM3 and HepG2 cells. Cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of EGCG for 24 h, stained with propidium iodide, and analyzed by flow cytometry. (C) HCC-LM3 and HepG2 cells were treated with different concentrations of EGCG, and the cell apoptosis rate was examined by flow cytometry. (D) Western blot analysis of cleaved-caspase 3 and PARP in HCC cells treated with EGCG (0, 50, and 100 μM). β-actin was used as a loading control. Plotted values represent the mean ± standard error of three independent experiments (n = 3) (*P < 0.05; +P < 0.01).