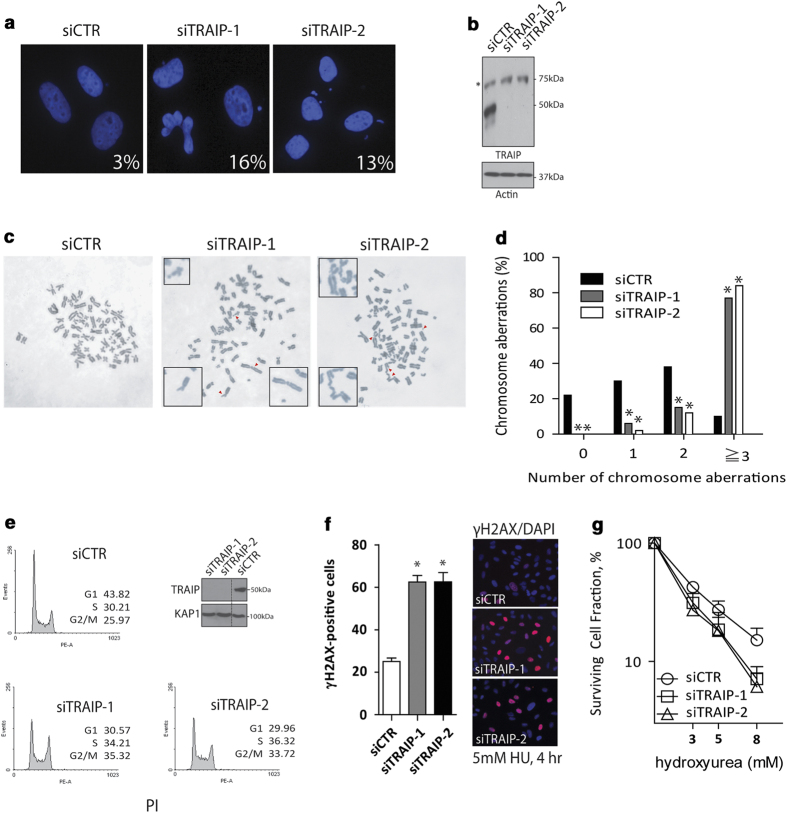
Figure 1.
TRAIP protects genome integrity. (a–d) Cells pre-treated with TRAIP-targeting siRNAs (siTRAIP-1 and siTRAIP-2) or non-targeting control siRNAs (siCTR) were challenged with hydroxyurea (5 mm, 4 h) and were subsequently processed for analysis of micronuclei formation frequencies (a), by western blotting to examine knockdown efficiencies (b), and frequency of chromosome aberrations (c, d). For each treatment group, we counted a total of 200 nuclei (a) or >100 metaphase spreads (c, d) from three independent experiments. We scored chromosome breaks and fusions as aberrations (c). *P<0.05 vs control. (e) Cell-cycle distribution was determined in U2OS cells depleted of TRAIP. Cells pre-treated with indicated siRNAs were fixed in 70% ethanol, stained with propidium iodide (PI), and were subjected to flow-cytometric analysis. (f) γH2AX positivity was determined in HU-challenged control or TRAIP-depleted cells by indirect immunofluorescence staining experiments using rabbit polyclonal anti-γH2AX antibodies. We scored cells positive for γH2AX when γH2AX foci >20 per nucleus. Results (mean±s.e.m.) were from three independent experiments with cell count n>200 each. *P<0.05 vs control. (g) Control or TRAIP-depleted cells were subjected to different doses of HU treatment in the clonogenic survival assay. Cells seeded on 60 mm dishes were incubated at indicated doses of HU-containing medium for 8 h. Results (mean±s.e.m.) were from three independent experiments each performed in triplicates.