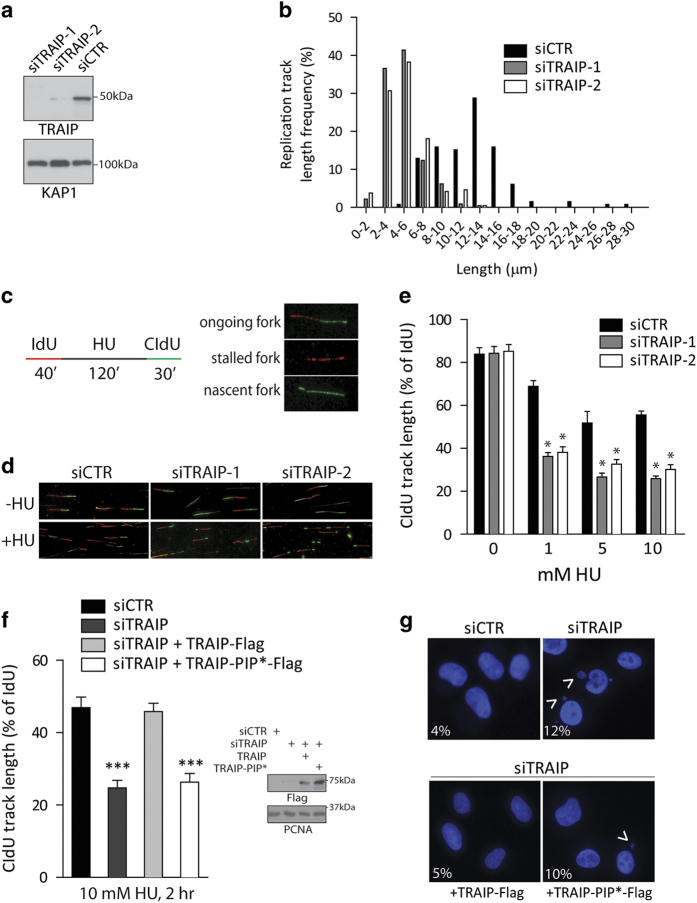
Figure 4.
TRAIP inactivation compromises DNA synthesis during replicative stress. (a, b) TRAIP-depleted cells displayed reduced rates of fork progression under replicative stress. Cells pre-treated with TRAIP-targeting siRNAs (siTRAIP-1 and siTRAIP-2) or control siRNAs (siCTR) were sequentially labeled with IdU then with CIdU in the presence of 5 mm hydroxyurea (HU). Western blotting experiments were performed to assess TRAIP silencing efficiency using anti-TRAIP antibodies. KAP1 was used as a loading control (a). DNA combing assays were performed to examine DNA synthesis, and length of CIdU tracks was determined (b) from three independent experiments. Note that IdU tracks did not differ among the treatment groups. (c–e) TRAIP promotes recovery of stalled forks. Schematic depicting experimental procedures involving sequential labeling with IdU and CIdU (c). DNA from cells pre-treated with TRAIP-specific siRNAs (siTRAIP-1 and siTRAIP-2) or control siRNAs (siCTR) was combed and immuno-labeled to determine fork progression with (+HU; 10 mm, 2 h) or without HU (−HU) treatment (d, e). Quantification of CIdU-labeled tracks relative to IdU tracks is shown for a range of HU doses. *P<0.05 vs control. (f) TRAIP promotes DNA replication restart via its PIP. Cells expressing siRNA-resistant TRAIP cDNAs (TRAIP-Flag or its PIP* mutant) were transfected with indicated siRNAs. As depicted in (c) cells were labeled with IdU, challenged with 10 mm HU (2 h), were labeled with CIdU before they were lysed and processed to assay for DNA synthesis. ***P<0.05 vs control. Western blot showing expression of TRAIP-Flag and mutant is shown. (g) Images showing micronuclei formation (arrow heads) in HU-challenged (5 mm, 4 h) cells pre-treated with control siRNA (siCTR), TRAIP-targeting siRNAs (siTRAIP), or in cells reconstituted with siRNA-resistant TRAIP cDNAs as in (f). Frequencies of micronuclei formation are shown. Results were derived from three individual experiments (n=200).