Fig. 1.
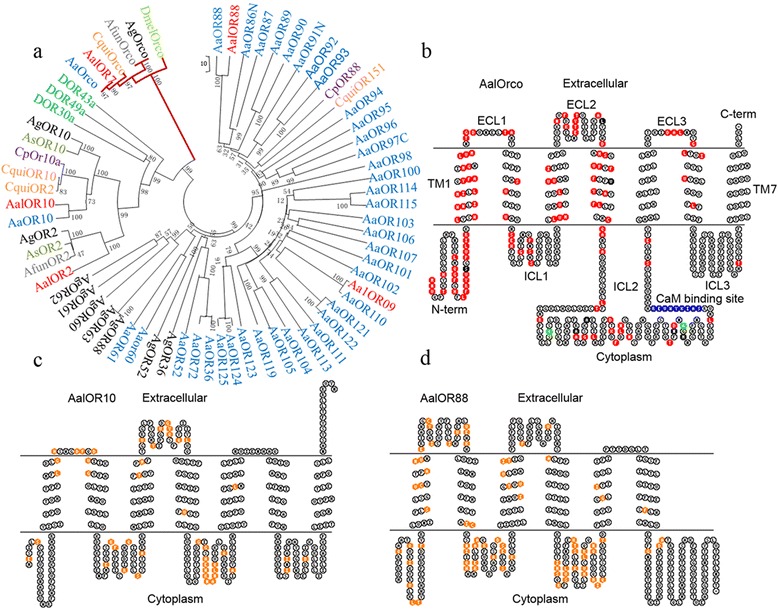
Phylogenetic relationships and transmembrane regions of four representative AalOR genes. a A neighbor-joining tree with AalOR 2, 7, 10 and 88 based on amino acid sequence alignment and constructed with MEGA5 using ClustalW. Key: Aedes albopictus, AalORs (red); Anopheles gambiae, AgORs (black); Culex quinquefasciatus, CquiORs (orange); Ae. aegypti, AaORs (blue); Cx pipiens pipiens, CpORs (violet); Drosophila melanogaster, DOR83b (green); An. funestus, AfunORs (gray); and An. stephensi AsORs (olive). b-d Transmembrane regions of AalORs predicted using HMMTOP and TMHMM. b The blue circles represent the CaM binding site, red circles indicate amino acids differing from the Dmel Orco ortholog, green circles indicate amino acids differing from AeOR7, and black circles represent those amino acids differing in both DmelOrco and AeOR7. c, d Orange circles represent amino acids that differ from the respective Ae. aegypti ortholog
