Figure 4. Quantification of various real samples (cells, serum and tissues) by the counting strategy.
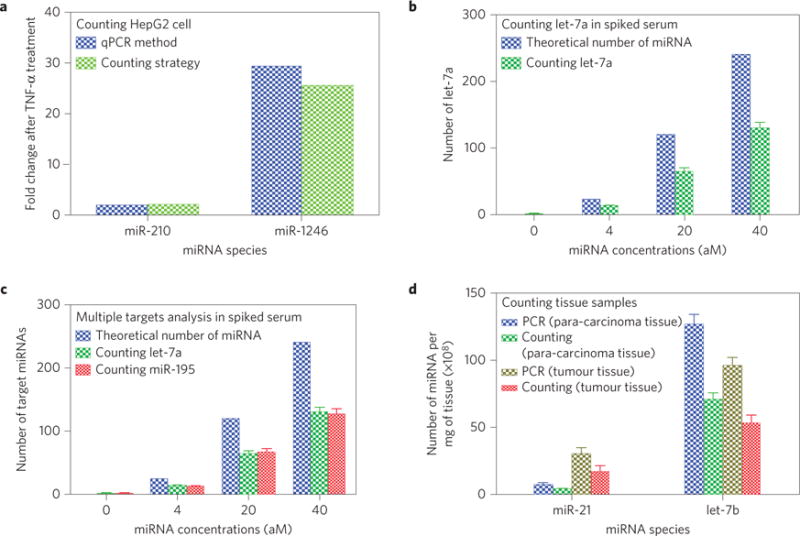
a, Fold change of the levels of each of the two miRNAs in HepG2 cancer cells after TNF-α treatment determined by our counting strategy and the qPCR method. A comparison between the two methods shows that the counting method can reliably determine the altered levels of miRNA expression due to chemical treatment of the cancer cells. b, Number of target miRNA (let-7a) in 10 μl of spiked human serum at various nominal concentrations determined by the counting method, as compared to the theoretical number. c, Number of target miRNAs (let-7a and miR-195) in 10 μl of spiked human serum at various nominal concentrations determined by the counting method, as compared to the theoretical number. To prepare the spiked serum samples in b and c, serum from a healthy person was made devoid of the target miRNAs (let-7a in b or both let-7a and miR-195 in c) by using a MMP probe functionalized with the sequence complementary to the target miRNAs to capture and magnetically remove the target miRNAs. Then a known amount of target miRNAs was added to form serum samples with specific concentrations of the target miRNAs. d, Numbers of two target miRNAs in 1 mg of the tissue (tumour or the surrounding healthy tissue) from a lung-cancer patient determined by the counting method and by qPCR. A comparison of the data from both methods confirms that the counting method is reliable in determining the level of miRNAs in the tissues of human cancer patients. The number of miRNAs was calculated by averaging the number obtained from three independent counting tests (p <0.05 with respect to the control).
