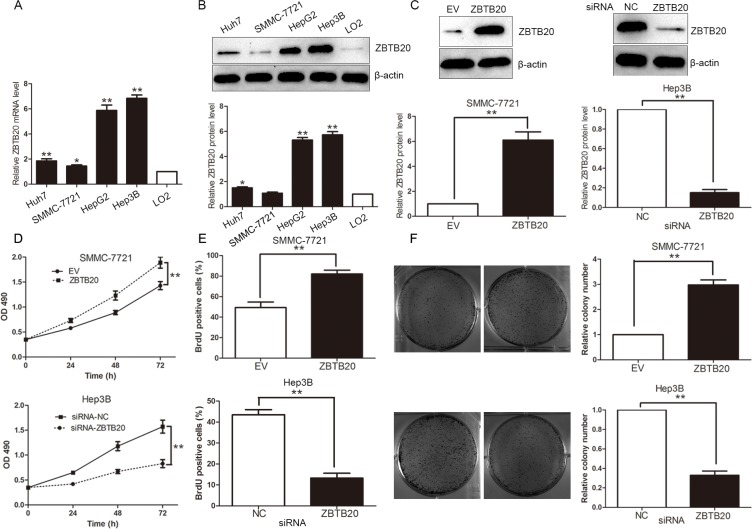
Figure 2. ZBTB20 facilitates proliferation and tumorigenicity of HCC cells.
(A and B) Comparing differences in the expression levels of ZBTB20 mRNA and protein between HCC cell lines with different proliferative potentials and the immortalized hepatic cell line. n = three repeats with similar results, *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 by ANOVA. (C) SMMC-7721 cells that were tranfected with empty vector (EV) or ZBTB20 retroviruses were subjected to immunoblotting for ZBTB20. ZBTB20 was knocked down by a specific siRNA and confirmed by Western blot in Hep3B cells. n = three repeats with similar results, **P < 0.01 by t test. (D) As assessed by MTT assays, ZBTB20 overexpression enhanced cell viability of SMMC-7721 cells and ZBTB20 knockdown was found to reduce Hep3B cell viability. n = three repeats with similar results, **P < 0.01 by ANOVA. (E) Cell proliferation as measured by BrdU incorporation assays was promoted by ZBTB20 overexpression in SMMC-7721 cells and suppressed by ZBTB20 knockdown in Hep3B cells. n = three repeats with similar results, **P < 0.01 by t test. (F) Representative colony formation assays were shown in HCC cells with altered ZBTB20 expression. Quantitative data disclosed that the ability of colony formation was enhanced after ZBTB20 overexpression in SMMC-7721 cells and reduced after ZBTB20 knockdown in Hep3B cells. n = three repeats with similar results, **P < 0.01 by t test.