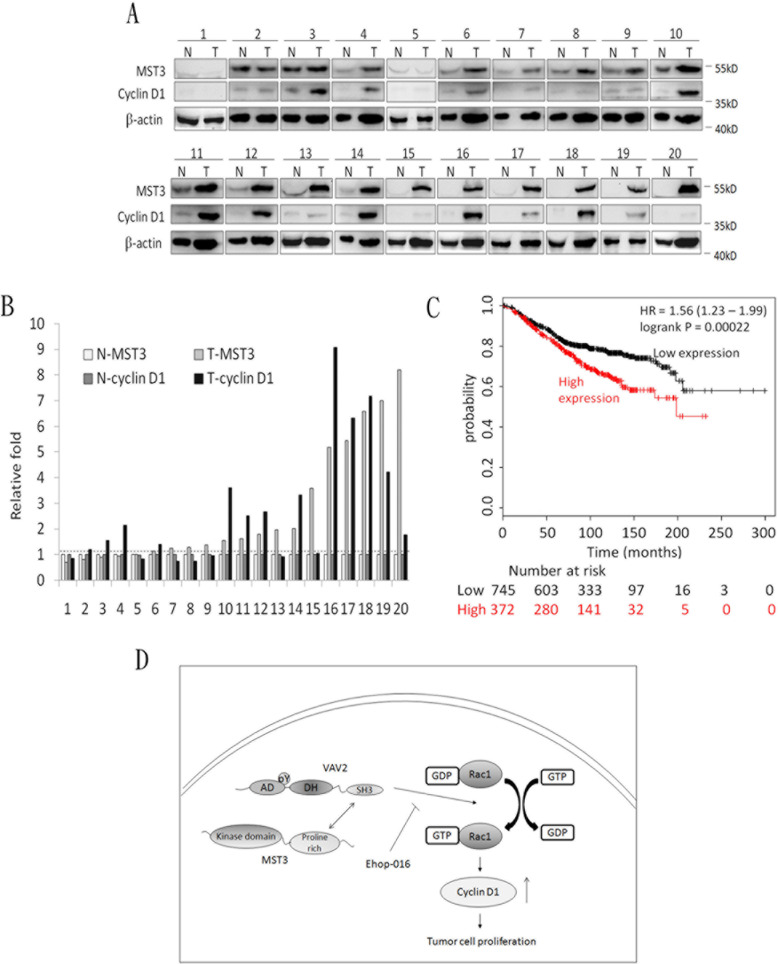
Figure 9. The co-overexpression of MST3 and cyclin D1 in breast tumor tissues.
A. Immunoblotting assay was used to determine the expression of MST3 and cyclin D1 in normal breast tissue (N) and breast tumor (T) specimens. Equal amounts (30μg) of protein from whole-tissue lysates were analyzed for MST3, cyclin D1 and β-actin expression by Western blotting analysis. B. Quantitative analysis of the MST3 and cyclin D1 protein level in normal breast tissue (N-MST3 and N-cyclin D1) and breast tumor (T-MST3 and T-cyclin D1) specimens. C. Kaplan-Meier analysis for overall survival in breast cancer patients (n = 1117) according to the co-expression of MST3 and cyclin D1. Auto select best cutoff was chosen in the analysis. The best specific probes (JetSet probes) that recognized MST3 and cyclin D1 which maps Affymetrix probe sets by selecting the best probe set for this analysis. High-level co-expression of MST3 and cyclin D1 was associated with decreased patient survival (log-rank P = 0.00022), and the hazard ratio (HR) (with 95% confidence intervals) was shown. D. Model for MST3 function in the VAV2/Rac1 signaling axis. The interaction of MST3 and VAV2 enhances tyrosine phosphorylation and activity of VAV2. Increased VAV2 activity activates Rac1-GTPase and induces cyclin D1 expression to promote tumor growth.