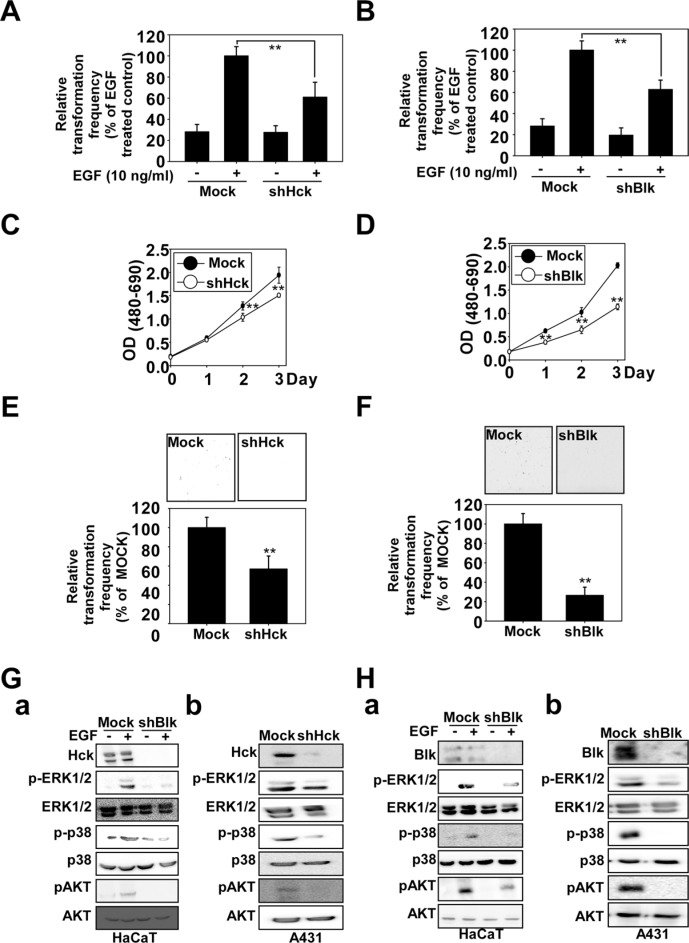
Figure 5. Knockdown of Hck or Blk inhibits EGF-induced neoplastic growth of HaCaT cells and growth of A431 cells.
A soft agar assay was performed using mock or (A) shBlk- or (B) shHck-transfected HaCaT cells and the number of colonies was counted under a microscope with the aid of the Image-Pro Plus software program (vs. 6.2). Knockdown of Blk or Hck decreases viability and inhibits anchorage-independent cell growth of A431 cells. Viability was evaluated by MTT assay using mock- or (C) shHck- or (D) shBlk- transfected A431 cells. A soft agar assay was performed using mock or (E) shHck - or (F) shBlk -transfected A431 cells. The asterisks (**) indicate a significant (**p < 0.01) difference between mock- and shHck- or shBlk-transfected cells. Knockdown of (G) Hck or (H) Blk regulates the Hck and Blk downstream signaling cascades. Knockdown of Hck or Blk inhibits ERK1/2, p38 and AKT phosphorylation in EGF-treated (a) HaCaT cells or (b) A431 cells. The cells were seeded and incubated for 48 h before proteins were recovered. Mock-, shHck- or shBlk-transfected HaCaT cells were treated with EGF (10 ng/ml) and harvested after 15 min. Immunoblotting was conducted using specific antibodies.