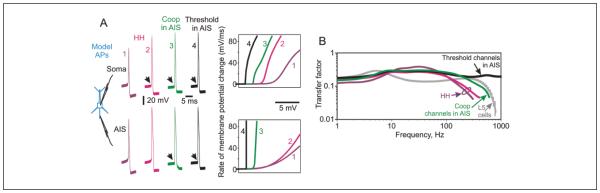
Figure 5.
Spike generation and frequency response function of multicompartment neuron models. (A) Action potentials in the soma and at the site of initiation in the axon initial segment (AIS) in four multicompartment models, and phase plots of the initial portions of these action potentials (APs). Black oblique arrows point at the sharp kink at AP onset. Note that in both models with Hodgkin-Huxley channels, AP onset is slow at the initiation site in the AIS, but becomes fast in the soma of the model with high density of sodium channels and increased Rax (magenta traces). In two other models, with a fraction of cooperative or threshold channels in the distal AIS, AP onset is fast both at the initiation site and in the soma. (B) Frequency response functions of the four models from A. Note the difference between the models in the ability to encode high frequencies. For comparison, gray line with error bars shows transfer function of layer 5 pyramidal neurons from Figure 4. All four models had the same morphology, with detailed structure of the axon initial segment and simple morphology of the dendrites (Baranauskas and others 2010), and same passive properties and Hodgkin-Huxley type potassium and sodium channels in the axon, soma and dendrites (Ilin and others 2013). The models differed in the channel composition in the initial segment. In the first two models (HH), the distal portion of the axon initial segment (30-50 µm from the soma) had a moderate (lilac traces, 2,000 pS/µm2) or very high (magenta traces, 20,000 pS/µm2) density of Hodgkin-Huxley type sodium channels. In the second model axial resistance in the axon was increased (Rax = 300 ohm cm compared with Rax = 150 ohm cm in other models). This combination of extreme values was necessary to achieve fast onset of AP in the soma, despite a slow, Hodgkin-Huxley type onset at the initiation zone in the distal initial segment (Baranauskas and others 2010). The distal AIS of the third model (Coop in AIS) had moderate density of sodium channels (2,000 pS/µm2), a small portion of which (10%) expressed cooperative activation (Naundorf and others 2006). Remaining sodium channels in the AIS and in other compartments were Hodgkin-Huxley type. In the distal AIS of the fourth model (Threshold in AIS), 10% of sodium channels expressed threshold activation. Details of model parameters are given in Ilin and others (2013), models 2, 6, 7, and 8 from Figure 3. Modified from Ilin and others (2013).