Figure 2. Morphine-induced generation of silent synapses is mediated by AMPAR internalization.
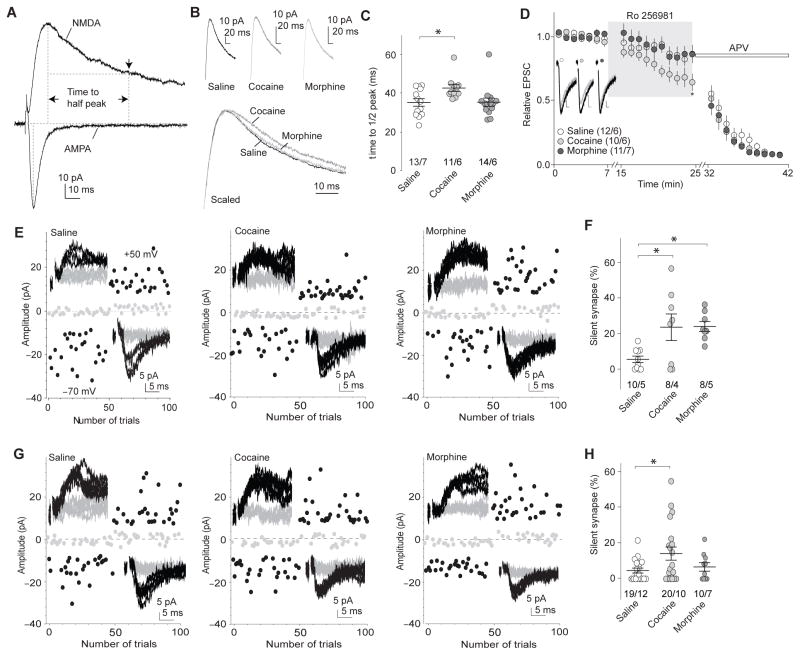
a Example traces (n=38 cells) showing that the decay kinetics of NMDAR EPSCs was measured by the half-decay time, the time elapsed from the peak amplitude to half peak amplitude. b Example NMDAR EPSCs in NAcSh MSNs 1d after saline (n=13/7 cells/rats), cocaine (n=11/6 cells/rats), or morphine (n=14/6 cells/rats) administration. c Summary showing that exposure to cocaine, but not morphine, prolonged the decay kinetics of NMDAR EPSCs (F2,35=4.25, p=0.02, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest). d Example traces and summary showing that Ro256981 (200nM) inhibited NMDAR EPSCs in NAcSh MSNs greater in cocaine-exposed rats (n=10/6 cells/rats) than in saline (n=12/6 cells/rats)- or morphine (n=11/7 cells/rats)-exposed rats (F2,810=15.71, p=0.00, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest). Following Ro256981, APV (50μM) was applied. Calibration bars: 10ms, 5pA. e Example EPSCs evoked by minimal stimulation and their trial plots in NAcSh MSNs from rats 1d after 5d co-administration of GluA2 scrambled peptide with saline (n=10/5 cells/rats), cocaine (n=8/4 cells/rats), or morphine (n=8/5 cells/rats). f Summary showing that co-administration of scrambled peptide did not affect cocaine- or morphine-induced generation of silent synapses (F2,23=6.15, p=0.01, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest). g Example EPSCs evoked by minimal stimulation and their trial plots in NAcSh MSNs from rats 1d after 5d co-administration of GluA23Y with saline (n=19/12 cells/rats), cocaine (n=20/10 cells/rats), or morphine (n=10/7 cells/rats). h Summary showing that co-administration of GluA23Y prevented morphine-, but not cocaine-induced generation of silent synapses (F2,46=3.44, p=0.04, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest). Error bar=s.e.m., *p<0.05, and **p<0.01.