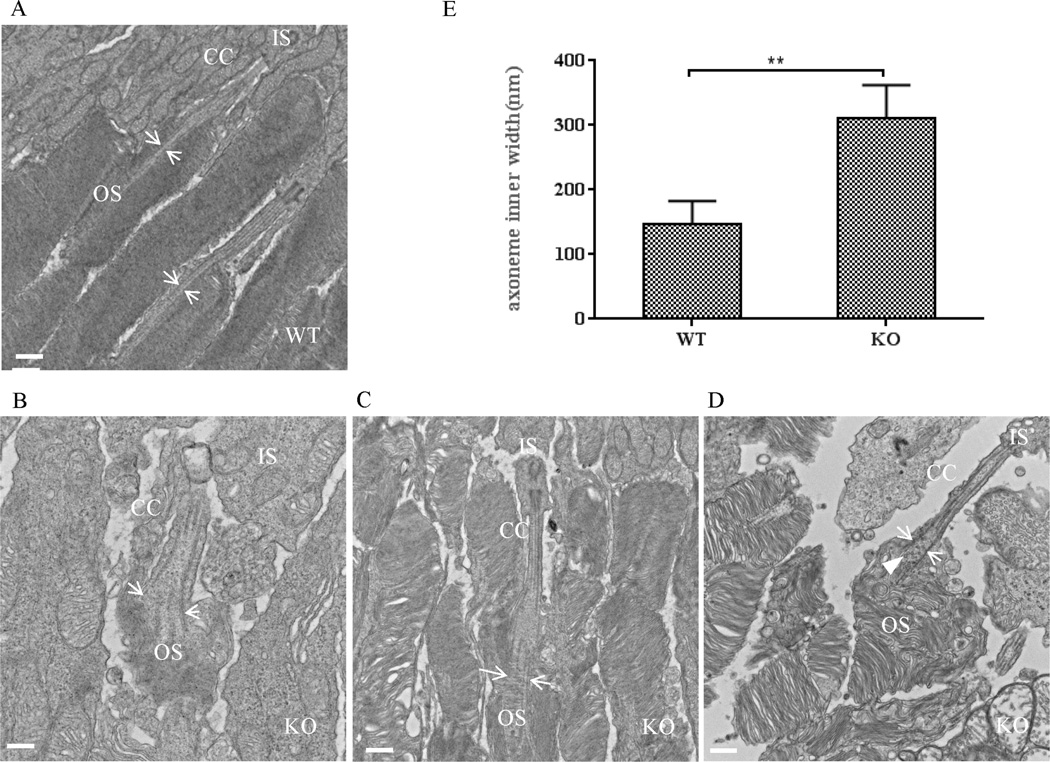
Fig. 6. The connecting cilium structure is modified in Lztfl1 knockout mouse retinas.
A–D: TEM characterization of wild-type (A) and Lztfl1 knockout (B–D) photoreceptor cells. The microtubule bundle of the distal axoneme was enlarged in the connecting cilium of knockout mice (arrows in B–D), compared to the wild-type photoreceptor cells (arrows in A). Some vesicles were visible in the open axoneme (arrowhead in D). Bars = 500 nm. E: Comparison of the inner width of the distal axoneme between wild-type and Lztfl1 knockout photoreceptor cells. The inner width (distance between the arrow pair) was measured from images generated by TEM (A–D). ** represents significant differences at P < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). OS, outer segment; IS, inner segment; CC, connecting cilium; WT, wild-type; KO, knockout.