Figure 1.
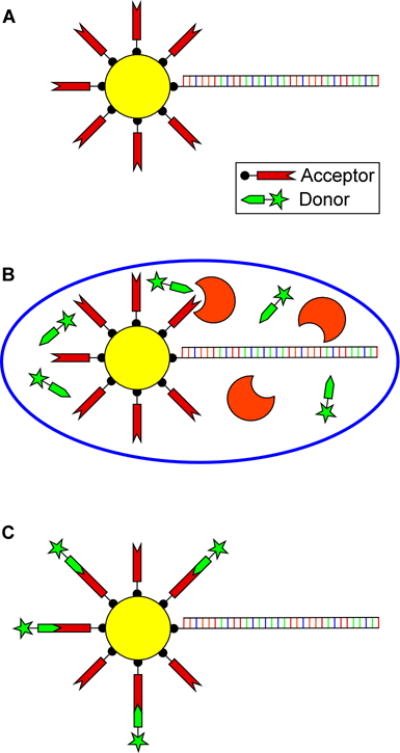
In vitro compartmentalization (IVC) based bead selection strategy. (A) Library DNA and the acceptor substrate are displayed on the surface of streptavidin coated microbeads. (B) These beads are then compartmentalized within a water in oil emulsion containing the components of an in vitro transcription and translation (TnT) reaction supplemented with the donor substrate. Beads with functional genes attached will be tagged with the reaction product on the bead’s surface. (C) Upon breaking the emulsion, the reaction product is labeled for detection and sorted based on fluorescence intensity. The recovered functional genes can then be reamplified using PCR for further screening.
