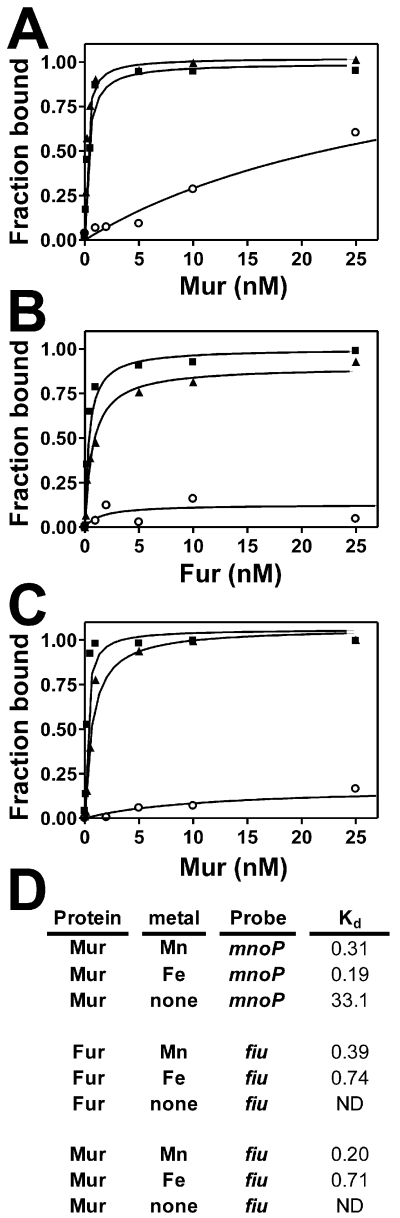
Fig 2.
Effects of Mn2+ and Fe2+ on binding of B. japonicum Mur or E. coli Fur to the mnoP or fiu promoter in vitro.
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) analysis was carried out using (A) B. japonicum Mur and 100 pmol mnoP containing the B. japonicum Mur binding site, (B) E. coli Fur and 100 pmol fiu containing the Fur binding site and (C) Mur and the fiu binding site. The binding reactions were carried out either with no metal (open circles), 100 μM Mn2+ (closed squares) or Fe2+ (closed triangles). Bound and unbound DNA were resolved on a 5% non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel and visualized by autoradiography. Autoradiographs were scanned, and bands were quantified. (D). Dissociation binding constants (Kd) were calculated from the binding data.