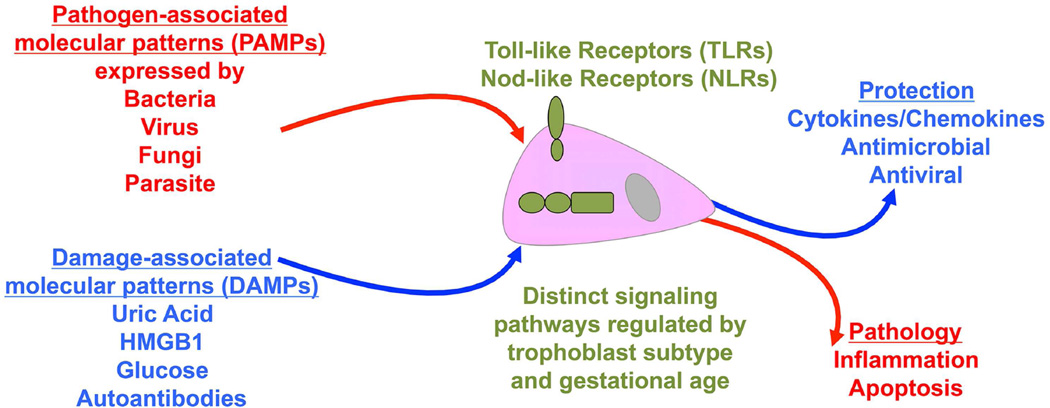
Figure 3. Innate immune sensing by the trophoblast.
Trophoblast cells sense infectious pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) expressed by bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites through their expression of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and Nod-like receptors (NLRs). Through these receptors, trophoblast cells also mount responses to non-infectious host-derived damage associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) such as uric acid, high mobility group B1 (HMGB-1), glucose and certain autoantibodies. Trophoblast expression of some TLRs and NLRs are regulated across gestation and cell subtype. Depending upon the trigger, receptor activated, and type of signaling pathway utilized, the trophoblast may mount either a regulated protective response that helps to maintain and promote a healthy pregnancy; or a damaging pathological response that might adversely impact pregnancy outcome.