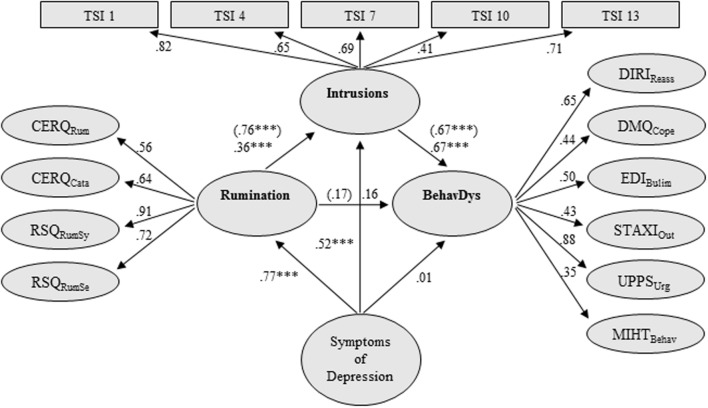
FIGURE 1.
Structural equation model (SEM) testing the mediational effect of intrusion on the relationship between rumination and behavioral dysregulation, controlling for symptoms of depression. Rumination = Rumination latent variable; BehavDys = Behavioral Dysregulation latent variable; TSI = Thought Suppression Inventory; Intrusions = Intrusions latent variable; CERQRum = Rumination scale of the Cognitive Emotion Regulation Questionnaire (shortened German version); CERQCata = Catastrophizing Scale of the Cognitive Emotion Regulation Questionnaire (shortened German version); RSQRumSy = Rumination about Symptoms of the Response Styles Questionnaire; RSQRumSe = Rumination about Self of the Response Styles Questionnaire; DIRIReass = Reassurance Seeking scale of the Depressive Interpersonal Relationships Inventory; DMQCope = Drinking to Cope scale of the Drinking Motives Questionnaire; EDIBulim = Bulimia scale of the Eating Disorder Inventory; STAXIOut = Anger-Out scale of the State-Trait Anger Expression Inventory; UPPSUrg = Urgency scale of the Urgency, Lack of Premeditation, Lack of Perseverance, Sensation Seeking-Impulsivity scale; MIHTBehav = Behavioral scale of the Multidimensional Inventory of Hypochondriacal Traits; Symptoms of Depression were quantified by the 9 items of the PHQ-9 (factor loadings: 0.65–0.86); all scales are latent variables; single items are not presented due to space limitations; values in brackets: β-regression weights in SEM without control of depressive symptoms; all factor loadings were significant on the 1% level; ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001; model fit: χ2(1999): 2790.02 (p < 0.001), CFI: 0.93, TLI: 0.93, and RMSEA: 0.031. R2 BehavDys: 0.65.