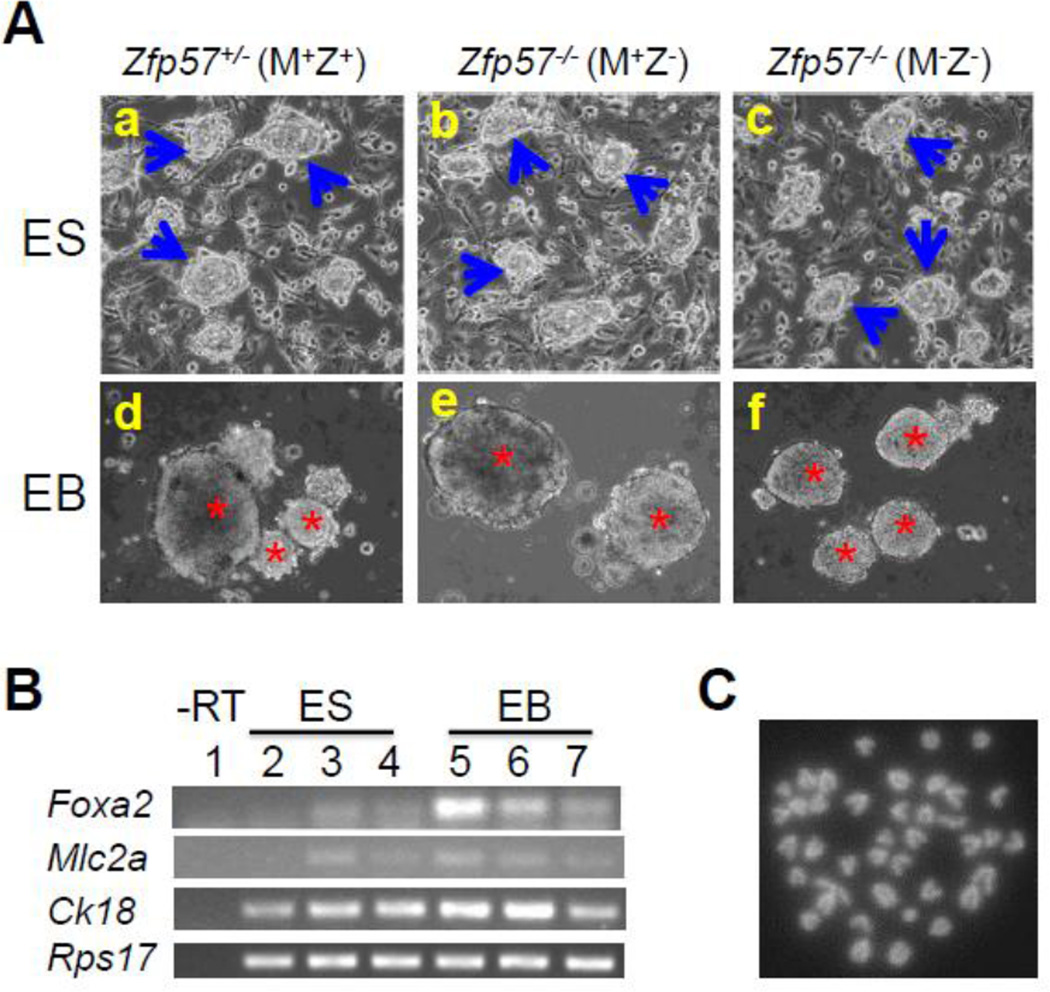
Figure 1. Blastocyst-derived ES clones display normal characters of ES cells.
A, ES clones on feeder cells (a-c) or EBs on non-adherent petri dish plates (d-f). One Zfp57+/− (M+Z+) ES clone (a, d) and one Zfp57−/− (M+Z−) ES clone (b, e) were shown here as the examples for the ES clones derived from the blastocysts generated from the cross between Zfp57+/− heterozygous female mice and Zfp57−/− homozygous male mice, whereas one Zfp57−/− (M−Z−) ES clone (c, f) shown here was an example for the ES clones derived from the cross between Zfp57−/− homozygous female mice and Zfp57−/− homozygous male mice. Blue arrows in a-c, undifferentiated ES cell colonies grown on feeder cells. Red asterisks in d-f, embryoid bodies (EBs) in suspension formed by ES cells plated on non-adherent petri dish plates. B, RT-PCR expression analysis of the marker genes in three ES clones and the EBs derived from these three ES clones after growing in suspension culture for 7–8 days. Lane 1, negative control without reverse transcription (-RT) of the same total RNA sample in Lane 4. Lane 2, ES cells of one Zfp57−/− (M−Z−) ES clone. Lanes 3–4, the ES cells of two Zfp57+/− (M+Z+) ES clones. Lane 5, EBs of the Zfp57−/− (M−Z−) ES clone. Lanes 6–7, EBs of two Zfp57+/− (M+Z+) ES clones. Foxa2, Mlc2a and Ck18 are markers for endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm, respectively. Rps17 is a house-keeping gene that was used as the loading control. C, DAPI-stained metaphase chromosome spread derived from a cell of one Zfp57−/− (M−Z−) ES clone. An example is provided here for the metaphase chromosome spread of five ES clones.